FIGURE 2.
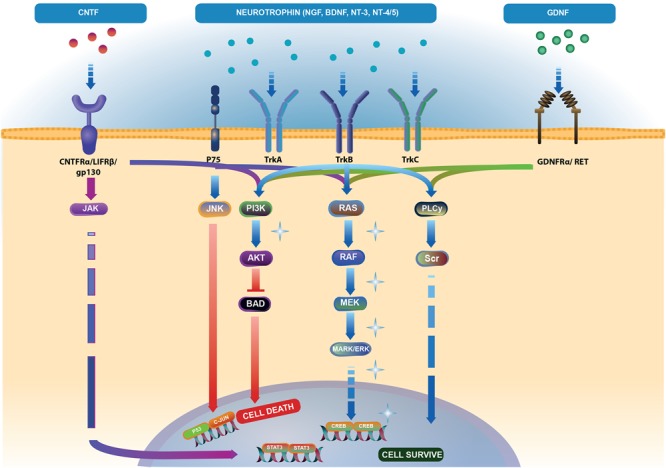
Neurotrophic factor (NTFs) signaling pathways. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5) bind to two families of receptors. Tropomyosin kinase (Trk) receptor binds with high affinity to promote cell survival via phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ), phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways (light blue arrows). Binding of NTFs to low affinity p75 receptor activates cell death through the JNK pathway (light blue and red arrows). Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) binding to CNTFRα receptor and two subunits – gp130 and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIFRβ) activate the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) (blue-violet arrows), MAPK and PI3K pathways (dark blue arrows). Binding of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) to the GDNFα receptor and tyrosine kinase RET receptor stimulates PLC-γ, MAPK and PI3K pathways (green arrows). Akt controls the activities of several proteins important in promoting cell survival, including substrates that directly regulate the caspase cascade, such as BAD. Phosphorylated BAD prevents its proapoptotic actions (Skaper, 2008) (red arrows). The pathway illustration was based on Reactome (https://reactome.org/ PMID: 29145629, PMID: 29077811). Represents the pathways responsible for endogenous cell-rescue mechanisms in glaucoma; these pathways were significantly activated when IOP was elevated, but decreased to baseline levels when IOP was lowered (Levkovitch-Verbin et al., 2007; Levkovitch-Verbin, 2015).
