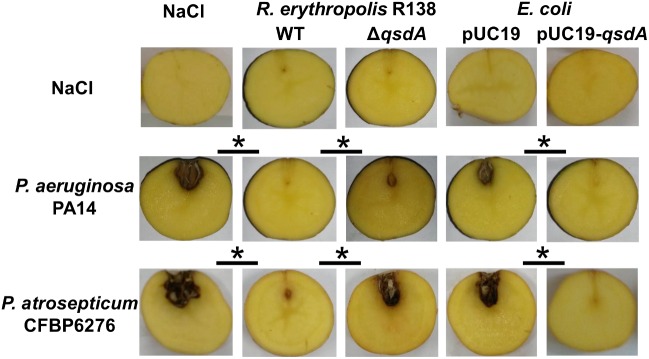
FIGURE 1.
Anti-virulence activity of Rhodococcus erythropolis and QsdA lactonase expressing E. coli strains against AHL-producing Gram-negative pathogens. Quorum quenchers and their corresponding control strains (R. erythropolis ΔqsdA mutant strain defective in QsdA lactonase production and E. coli pUC19) were compared for biocontrol activity against a 3-oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL producer, the human pathogen P. aeruginosa PA14, as well as a 3-oxo-C8-HSL producer, the potato pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum CFBP6276. Seven days after inoculation in potato tubers, tissue necrosis or soft-rot due to P. aeruginosa and P. atrosepticum, respectively, were analyzed and compared between tuber lots (black bars). For the controls, one or both strains were replaced in the inoculum with a 0.9% NaCl solution. Significant differences (Mann and Whitney test; p-value < 0.01) in maceration symptoms between infected tubers inoculated with control and quorum quencher strains are indicated with an asterisk.