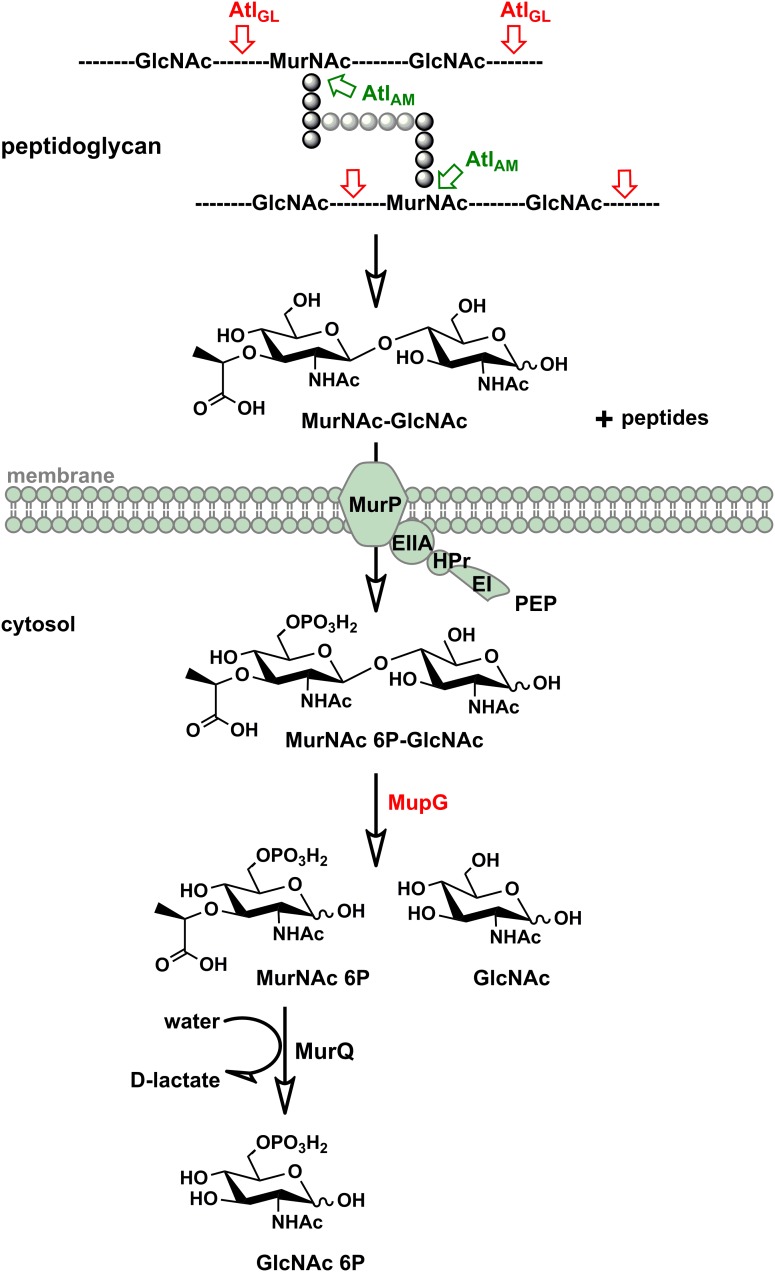
FIGURE 7.
Scheme of the peptidoglycan sugar recycling in S. aureus. During growth and division, S. aureus cells constantly degrade and resynthesize their peptidoglycan. The major autolysin Atl, a bifunctional muramoyl-L-alanine amidase and endo-N-acetylglucosaminidase, is able to cleave its peptidoglycan, generating MurNAc-GlcNAc and peptide turnover products. MurNAc-GlcNAc disaccharide is reutilized: transported in the cells and concommitantly phosphorylated by the MurP PTS transporter generating intracellularly MurNAc 6P-GlcNAc. Subsequently, the MurNAc 6-phosphate-GlcNAc glycosidase MupG cleaves this compound, generating the products MurNAc 6P and GlcNAc. The D-lactyl ether substituent of MurNAc 6P is specifically cleaved off by the etherase MurQ, previously characterized in our lab, forming GlcNAc 6P and D-lactate (Borisova et al., 2016). It is currently unclear how GlcNAc, the second product of the MupG reaction, is further metabolized in S. aureus cells.