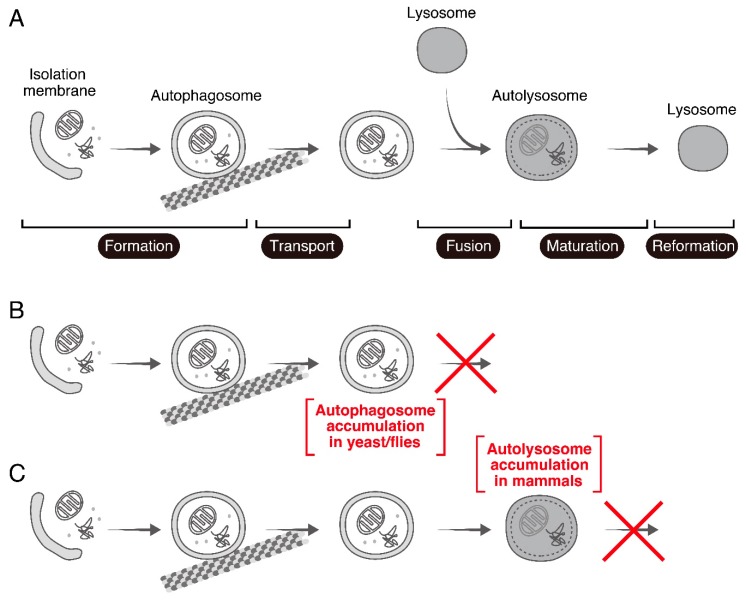
Figure 1.
Overview of autophagy and the autophagic phenotypes reported in Rab7-KO yeast/fruit flies and mammals. (A) Overview of autophagy. Upon induction of autophagy by stresses such as nutrient starvation, an isolation membrane emerges in the cytoplasm and sequesters cytoplasmic contents to form an autophagosome (formation step). The autophagosome is delivered to the perinuclear region along microtubules (transport step), where it fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome (fusion step). Energy is supplied by degradation of the cargos sequestered in the autolysosome (maturation step), and, finally, a new lysosome is formed (reformation step). (B) Accumulation of autophagosomes in Ypt7-KO yeast and Rab7-KD fruit flies, suggesting that Rab7/Ypt7 regulates the autophagosome-lysosome fusion step. (C) Accumulation of autolysosomes in Rab7-KO mammalian cultured cells, suggesting that mammalian Rab7 regulates the autolysosome maturation step.