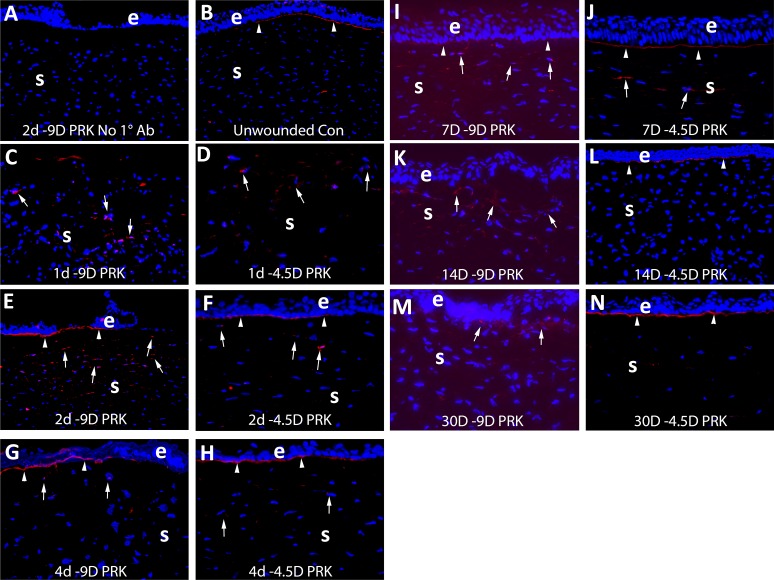
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemistry for perlecan protein expression in control unwounded corneas and at time points after −4.5- and −9-D PRK in rabbits. e is epithelium and S is stroma in each panel. Blue is DAPI staining of all nuclei in all panels. In each case, the panel shown is representative of the results noted in three corneas at each time point in each group. (A) Example control staining (this example at 2 days after −9-D PRK) with no primary antibody. (B) In unwounded control corneas perlecan was detected in the EBM (arrowheads) but little was detected in stromal cells. At (C) 1 day after −9-D PRK (D) 1 day after −4.5-D PRK, perlecan protein production was present in some stromal cells (arrows). At (E) 2 days after −9-D PRK, (F) 2 days after −4.5-D PRK, (G) 4 days after −9-D PRK, or (H) 4 days after −4.5-D PRK there was similar perlecan in the nascent EBM (arrowheads) and stromal cells (arrows). At 7 days after −9-D PRK, a change was noted in subepithelial EBM perlecan (arrowheads) in the (I) −9-D PRK corneas compared with the (J) −4.5-D PRK corneas. At 14 days, after the difference in the subepithelial perlecan (arrowheads) between (K) −9-D and (L) −4.5-D PRK was even more pronounced. Perlecan was detected in anterior stromal cells in both groups (arrows). At (M) 30 days after −9-D PRK there continued to be no subepithelial linear EBM perlecan, although perlecan was detected in cells in the anterior stroma (arrows). In contrast, in corneas (N) at 30 days after −4.5-D PRK, the linear EBM-associated perlecan (arrowheads) was present and there was relatively little perlecan present in stromal cells. Magnification ×200 in all panels.