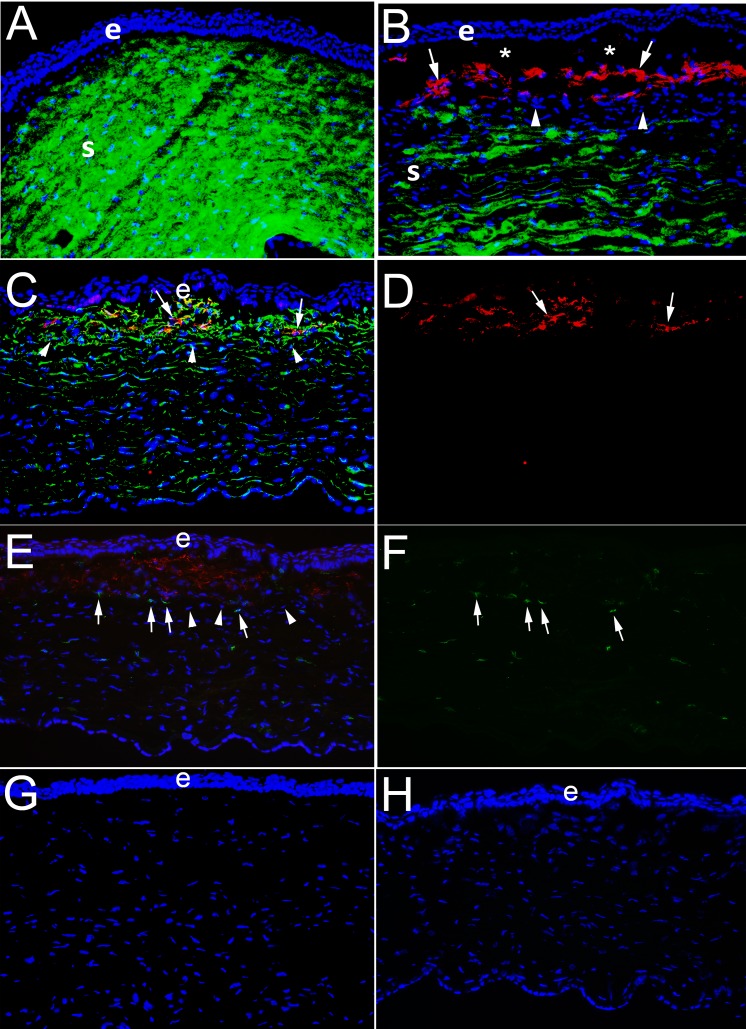
Figure 4.
IHC for the keratocyte marker keratocan, myofibroblast marker α-SMA, vimentin, and CD45 in corneas at 1 month after PRK in rabbits. e is epithelium and S is stroma. (A) At 1 month after −4.5-D PRK, duplex IHC shows keratocan41 (green) is homogeneously distributed in keratocytes and throughout the stroma and no α-SMA is detected. (B) In contrast, at 1 month after −9-D PRK, when corneas have dense subepithelial fibrosis at the slit lamp (not shown) duplex straining shows α-SMA (red)+ keratocan− myofibroblasts (arrows) present in the subepithelial anterior stroma. Beneath this layer of myofibroblasts, there are keratocan+ α-SMA− keratocytes, although the keratocan staining in the stroma is less homogeneous than in −4.5-D PRK corneas. *Artifactual separation of the epithelium from the stroma that commonly occurs during cryostat sectioning of corneas with anterior myofibroblasts and fibrosis due to poor adhesion between the epithelium and the stromal surface. In a control IHC for keratocan and α-SMA on a section from a −9-D PRK cornea at 1 month after surgery in which both primary antibodies were excluded there was no nonspecific staining (not shown). (C) Duplex IHC for vimentin and SMA in a –9-D PRK cornea at 1 month after surgery shows α-SMA+ myofibroblasts (arrows) are also vimentin+, as expected. Keratocytes deeper in the cornea are weakly vimentin+. Also, most, if not all, of the cells in the band (arrowheads) between myofibroblasts and keratocytes seen in (B) are also vimentin+. (D) The same image as (C), except showing only α-SMA+ red, better shows the position of the myofibroblasts (arrows). (E) Duplex IHC for α-SMA and CD45 in a –9-D PRK cornea at one month after surgery shows some of the cells within the band beneath the α-SMA+ myofibroblasts are CD45+ (arrows), but others are CD45− (arrowheads). Some α-SMA+ myofibroblasts are also CD45+, indicating these myofibroblasts likely developed from fibrocytes that migrated into the cornea. Keratocytes are CD45−, but some CD45+ cells are noted in this posterior area that are bone marrow–derived cells that migrated into the stroma after injury. (F) The same image as (E), except showing only CD45+ cells and it better shows they are present beneath the anterior zone populated with α-SMA+ myofibroblasts, but also among the α-SMA+ myofibroblasts in the anterior stroma and keratocytes in the posterior stroma. (G) Control duplex IHC for vimentin and α-SMA without either primary antibody shows no nonspecific staining. (H) Control duplex IHC for CD45 and α-SMA without either primary antibody shows no nonspecific staining. All magnifications are ×200.