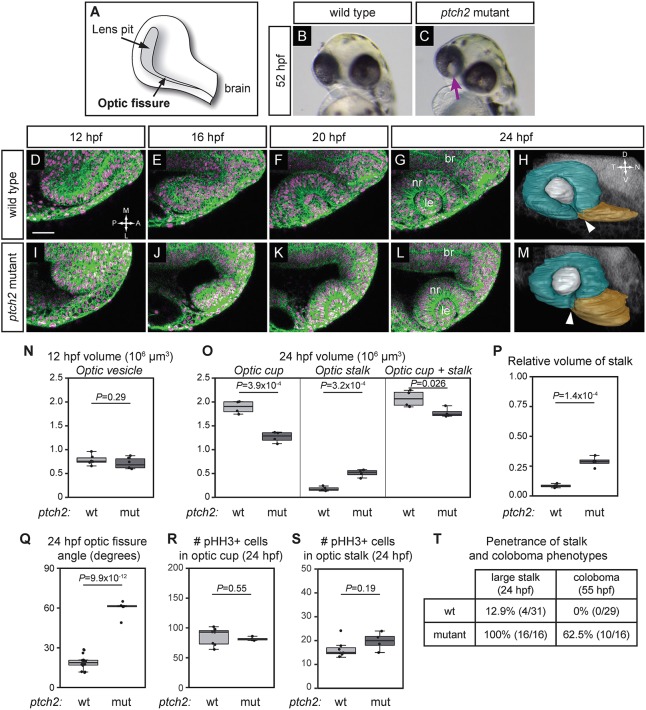
Fig. 1.
Optic cup morphogenesis and optic fissure and stalk formation are disrupted in the ptch2tc294z mutant. (A) Schematic of optic fissure at optic cup stage, 24 hpf. (B) Wild-type embryo, 52 hpf: the eye is evenly pigmented. (C) ptch2tc294z mutant embryo, 52 hpf: coloboma is apparent as a region of hypopigmentation in the eye (arrow). (D-G,I-L) Wild-type (D-G) and ptch2tc294z mutant (I-L) optic cup formation, single confocal slices from four-dimensional imaging data set (12-24 hpf). Dorsal view. Green, EGFP-CAAX (membranes); magenta, H2A.F/Z-mCherry (nuclei). (H,M) Volume rendering of wild-type (H) and ptch2tc294z mutant (M) embryos, 24 hpf. Lateral view. Teal, optic cup; gray, lens; gold, optic stalk. Arrowhead indicates the optic fissure, which has not formed correctly in the mutant. (N) Optic vesicle volume in wild-type (wt) and ptch2tc294z mutant (mut) embryos, 12 hpf. n=6 for each genotype. (O) Optic cup, stalk, and total volume, 24 hpf. n=4 for each genotype. (P) Relative volume of stalk as a proportion of optic cup+stalk volume. n=4 for each genotype. (Q) Angle measurement of optic fissure opening, 24 hpf. n=16 wt, 5 mut. (R,S) Number of phospho-histone H3-positive cells in the optic cup (R) and stalk (S), 24 hpf. n=7 wt, 4 mut. (T) Comparison of penetrance of large stalk and coloboma phenotypes at 24 and 55 hpf, respectively. (N,O,Q,S) Unpaired Student's t-test. (P,R) Unpaired Welch's t-test to account for unequal variance. br, brain; le, lens; nr, neural retina. RPE is very flattened and difficult to see; thus it is not labeled. Scale bar: 50 µm.