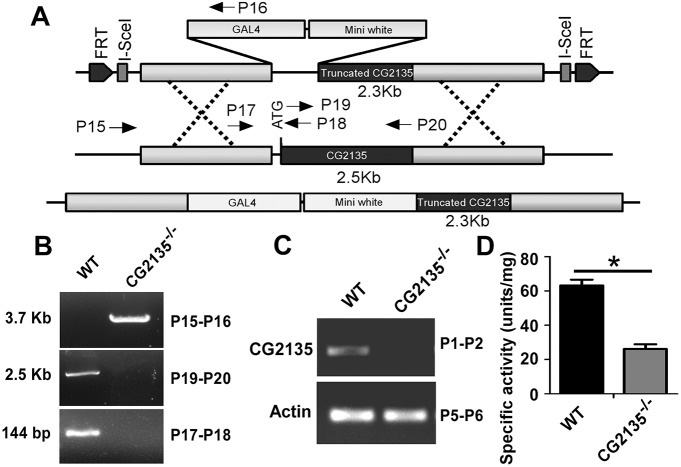
Fig. 2.
Generation of the CG2135−/− fly. (A) Schematic representation of the linearized CG2135 knockout construct containing Gal4 and mini-white markers flanked by 5′ and 3′ genomic regions of CG2135 with a truncation of a 212-bp fragment. FRT and I-SceI sites are also shown. The targeted allele after homologous recombination is shown at the bottom. Primer binding sites are indicated by arrows. (B) Genotype of the wild-type (WT) and the CG2135−/− fly was verified by genomic PCR. Integration of the Gal4 marker gene in the CG2135−/− fly was confirmed by PCR amplification of the 3.7-kb product with P15-P16 primers. Deletion of the genomic fragment in the CG2135−/− fly was verified by the absence of any PCR products with P19-P20 and P17-P18 primer sets. The 2.5-kb and 144-bp PCR products were amplified in the WT fly, as expected. (C) RT-PCR with CG2135-specific primer sets (P1-P2), showing absence of the CG2135 mRNA in the CG2135−/− fly. RT-PCR with actin amplification (P5-P6) served as control. (D) β-GUS-specific activity in the WT and CG2135−/− fly. Error bars represent s.e.m. of values from three independent experiments. *P≤0.05.