Figure 1.
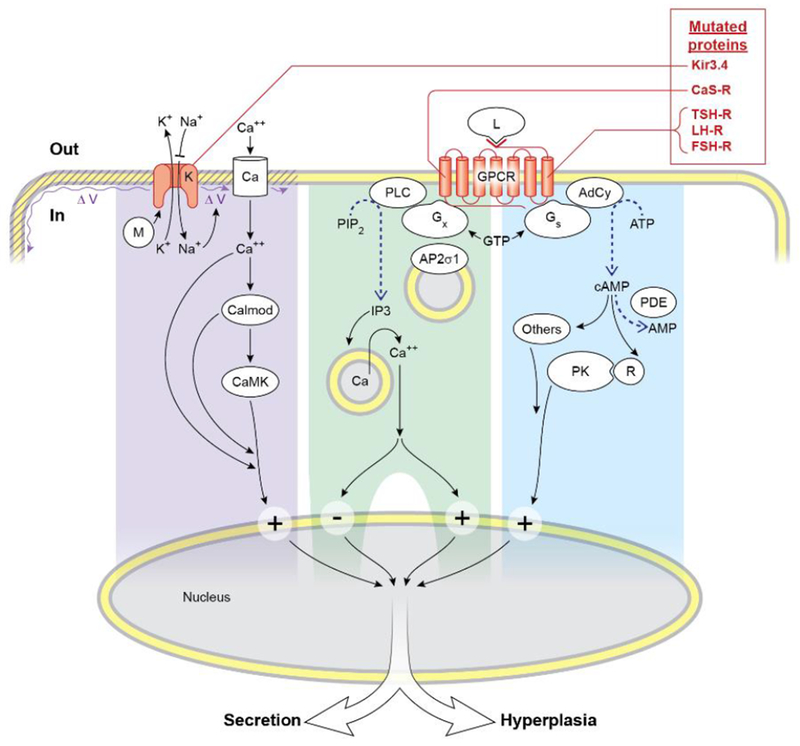
Overview of parts of the signaling pathways of the five mutated proteins in the 5 syndromes of this review. The mutated K+ channel (or Kir3.4) is shown with abnormally decreased ion selectivity of its mutation, so that fluxes of K+ and Na+ are in directions reversed from normal. Mutated proteins causing syndromes of this review are shown in red. Early downstream parts of each of three pathways are highlighted by a different background color. The pathway from Gx divides and includes a large plus or minus sign to illustrate that the CaS-R has opposite downstream effects in the parathyroid cell versus in the C-cell. By mostly unknown mechanisms, the four pathways likely converge downstream to regulate secretion and hyperplasia.
Abbreviations: G-protein coupled receptor GPCR; Calmodulin Calmod; Calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase CaMK; Ion channels K or Ca; Phospholipase C PLC; Sigma subunit of AP2S1 AP2σ1; Adenylyl cyclase Ad Cy; Ligand L; Heterotrimeric stimulatory G-protein Gs; Heterotrimeric G-protein other than Gs Gx; GTP-binding protein modulator of Kir3.4 M; Phosphatidyl inositol diphosphate PIP2; Inositol triphosphate IP3; Phospho-diesterase PDE; Protein kinase A catalytic subunit A PK; Regulatory inhibitory subunit 1A of PKA R; Voltage of plasma membrane V.
