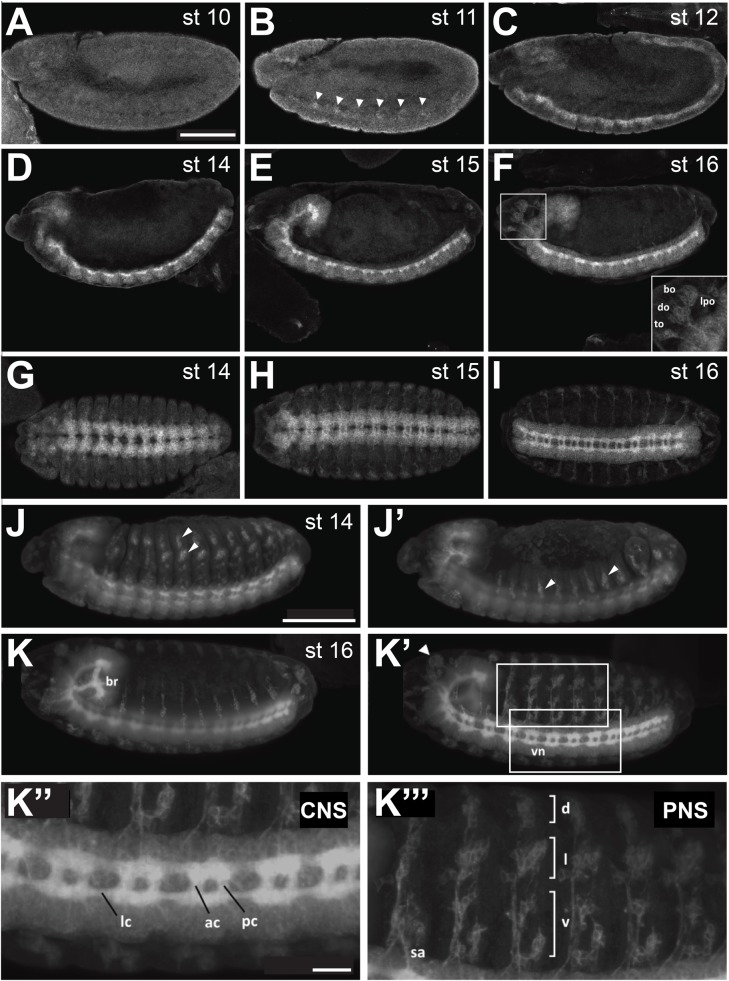
Fig. 1.
Expression of a Ror-eGFP fusion protein under control of the endogenous Ror promoter in Drosophila embryos. (A-F) Lateral views of stage 10-12 and 14-16 embryos. (G-I) Stage 14-16 embryos viewed from the ventral side, anterior to the left. (J-K‴) Light sheet fluorescence microscopy images of Ror-eGFP embryos. The images show maximum intensity projections of stacks taken from whole embryos. (J,J′) and (K,K′) show the same embryo, respectively, scanned from both sides. (J,J′) At stage 14 Ror-eGFP expression is strong in the embryonic CNS and already visible in the developing PNS. (K,K′) At stage 16 Ror-eGFP is expressed throughout the entire nervous system. (K″) Enlarged view of the CNS seen in (K′). (K‴) Enlarged view of the PNS seen in (K′). Areas shown at higher magnification in (K″) and (K‴) are indicated by boxes in (K′). Scale bars for A-K′: 100 µm; K″,K‴: 20 µm. bo, bolwig's organ; do, dorsal organ; to, terminal organ; lpo, lateropharyngeal organ; br, embryonic brain; vn, ventral nerve cord; lc, longitudinal connectives; ac, anterior commissures; pc, posterior commissures; sa, sensory axon; d, dorsal cluster; l, lateral cluster; v, ventral cluster. In (A-F) and (J-K′) anterior is to the left and dorsal up. Arrowheads in (B) point to the first cell clusters showing Ror-eGFP expression during embryonic development. Arrowheads in (J, J′ and K′) point to sensilla of the PNS.