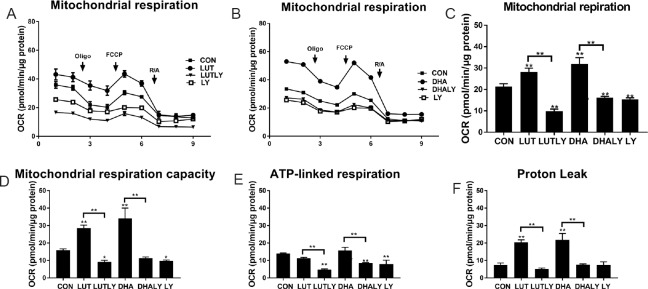
Figure 4.
Lutein or DHA treatment increases mitochondrial function
(A) Lutein-mediated increased mitochondrial respiration and was reversed by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 co-treatment. (B) DHA-mediated increased mitochondrial respiration and was reversed by LY294002 co-treatment. (C) Quantification of mitochondrial respiration by subtracting non-mitochondrial OCR (after adding R/A) from OCR before adding oligomycin (F(5,11) = 88.9, P < 0.01). (D) Quantification of mitochondrial maximum capacity by subtracting non-mitochondrial OCR (after adding R/A) from OCR after adding FCCP (F(5,11) = 68, P < 0.01). (E) Quantification of ATP linked respiration by subtracting non-mitochondrial OCR (after adding R/A) from OCR after adding oligomycin (F(5,11) = 32.5, P < 0.01). (F) Quantification of proton leak by subtracting non-mitochondrial OCR (after adding R/A) from OCR before adding FCCP (F(5,11) = 55.5, P < 0.01). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, vs. CON (one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference post hoc test), data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, three replications in each group. OCR: Oxygen consumption rate; FCCP: carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone; Oligo: oligomycin (2 μM); R/A: rotenone and antiomycin (1 μM); CON: control; LUT: lutein (5 μM); LUTLY: lutein (5 μM) + LY294002 (10 μM); DHA: docosahexaenoic acid (10 μM); DHALY: DHA (10 μM) + LY294002 (10 μM); LY: LY294002 (10 μM).