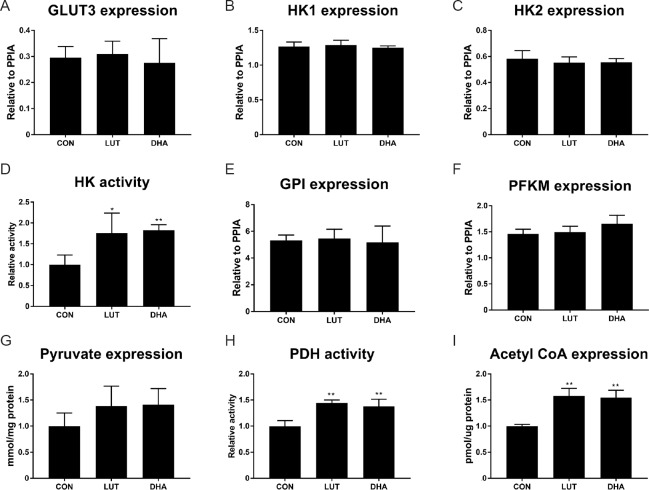
Figure 6.
Effect of lutein on glycolytic enzymes and intermediates.
After treatment of 5 μM lutein or 10 μM DHA for 3 days, total RNA was extracted from SH-SY5Y cells and mRNA levels of glucose transporter 3 (A, GLUT3), hexokinase 1 (B, HK1), hexokinase 2 (C, HK2), glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (E, GPI), phosphofructokinase, muscle (F, PFKM) were assessed by qPCR. For the measurement of enzymatic activity and metabolic intermediates, SH-SY5Y cells were harvested after treatment, and cell lysate were used to measure intracellular enzymatic activities (relative to control) as described in methods: (D) The activity of HK (F(2,9) = 8.2, P < 0.01); (H) the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) (F(2,9) = 20.9, P < 0.01); (G) concentration of pyruvate (F(2,9) = 2.1, P = 0.18); (I) concentration of acetyl-CoA (F(2,9)=29.1, P < 0.01). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. untreated control cells (one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference post hoc test), data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, four replications in each group. DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; CON: control; LUT: lutein.