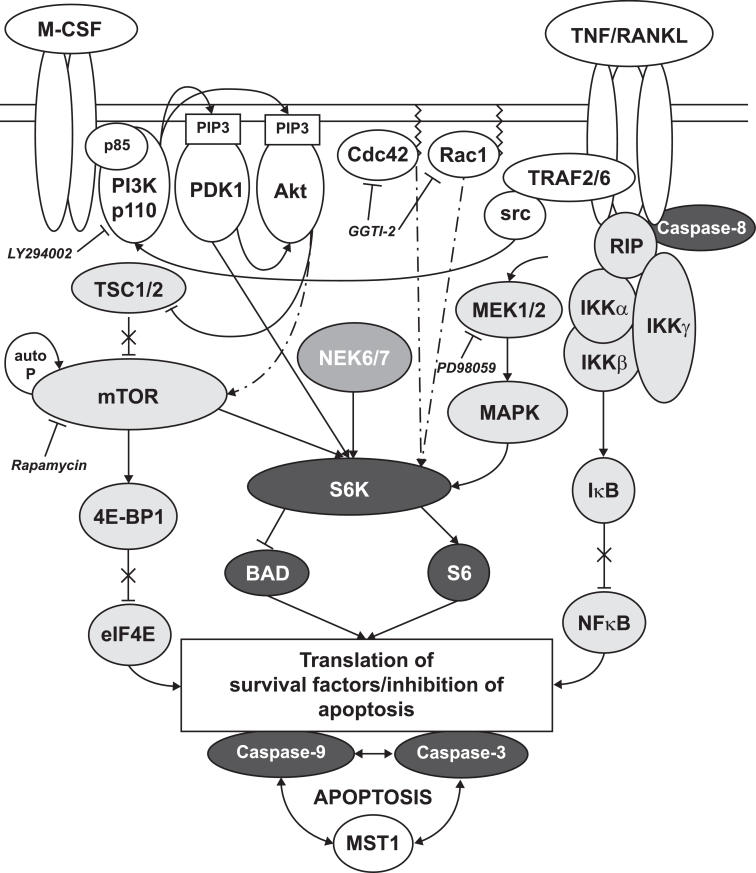
Fig. 4.
Schematic illustration of mTOR/S6K intracellular signal transduction pathways in the osteoclast [16]. M-CSF and RANKL are required for osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast activation. Upon activation of their respective receptors, M-CSF-R and RANK, downstream signaling pathways are activated. Signals converge on the mTOR/S6K axis. Upon mTOR inhibition, suppression of this pathway leads to osteoclast apoptosis and thereby reduced bone resorption. Abbreviations: Akt, protein kinase B; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; P, phosphate; RANK, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; S6K, 40 S ribosomal S6 kinase; src, steroid receptor coactivator; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TSC tuberous sclerosis complex.