Fig. 2. Functional partnership between group-II and group-I mGlu receptors in mouse cortical slices at different developmental ages.
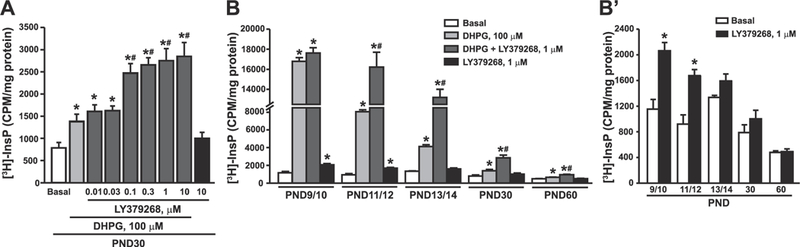
Concentration-dependent amplification of DHPG-stimulated PI hydrolysis by LY379268 in cortical slices of mice at PND30 is shown in (A). The age-dependent profile of DHPG-stimulated PI hydrolysis in the absence or presence of LY379268 is shown in (B). Data with LY379268 alone are highlighted in (B′). Values are mean ± S.E.M. of 3–4 determinations. p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA + Fisher’s LSD in A and B and Student’s t-test in B′) vs. the respective basal (*), DHPG (#). (A): F(8,27) = 22.49; (B): F(3,11) = 840.6 (PND9/10); F(3, 8) = 132.27 (PND11/12); F(3,8) = 263.84 (PND13/14); F(3,12) = 29.46 (PND30); F(3,12) = 45.25 (PND60); (B′): t(5) = −4.84 (PND9/10); t(4) = −5.32 (PND11/12).
