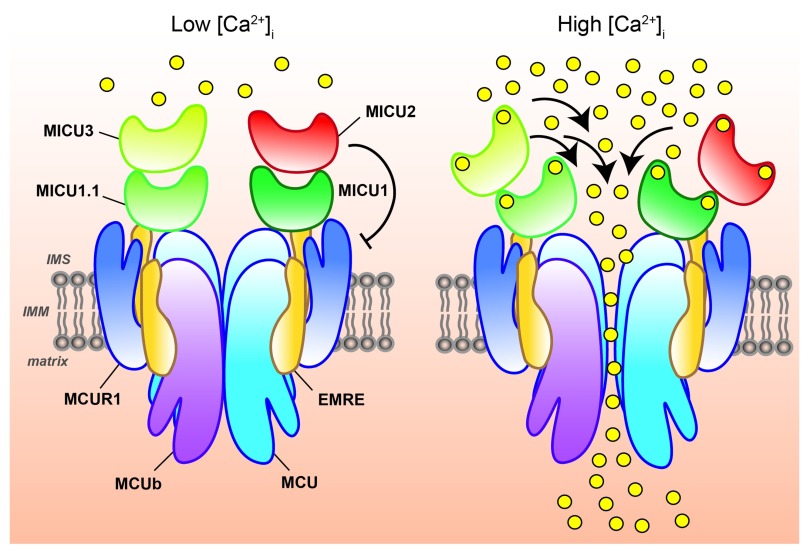
Figure 1. The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex.
Schematic representation of MCU-mediated Ca 2+ entry into mitochondria at different intracellular Ca 2+ concentrations ([Ca 2+] i). Mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake is controlled by a multiprotein complex consisting of MCU and MCUb (the pore-forming subunits) together with the essential mitochondrial Ca 2+ uniporter regulator (EMRE), the mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake (MICU) proteins, MICU1, MICU1.1, MICU2, and MICU3, and, possibly, the MCU regulator 1 (MCUR1). At low [Ca 2+] i, MICU1/MICU1.1–MICU2 or MICU1/MICU1.1–MICU3 heterodimers ensure MCU gatekeeper activity, preventing undesirable mitochondrial Ca 2+ cycling in resting cells. At high [Ca 2+] i, the MICU proteins act as positive regulators of MCU channel activity, allowing efficient mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake (right). IMS, intermembrane space; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane.