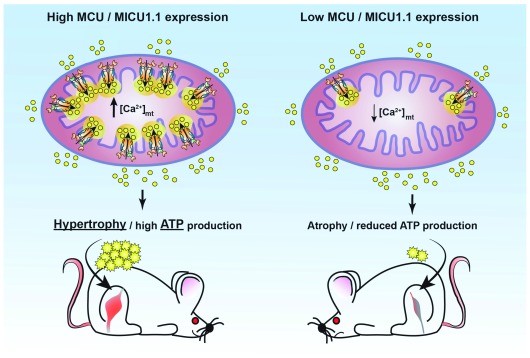
Figure 2. The role of mitochondrial Ca 2+ signalling in skeletal muscle trophism.
Schematic representation of the effects of manipulating mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake in skeletal muscle fibres. Increased mitochondrial Ca 2+ accumulation by enhanced expression of mitochondrial Ca 2+ uniporter (MCU) or mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake protein 1.1 (MICU1.1) leads to muscle hypertrophy by stimulating fibre growth and ATP production (left). Reduction of mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake by downregulation of either MCU or MICU1.1 causes fibre atrophy and impaired ATP production (right). [Ca 2+] mt, mitochondrial Ca 2+ concentration.