Figure 5.
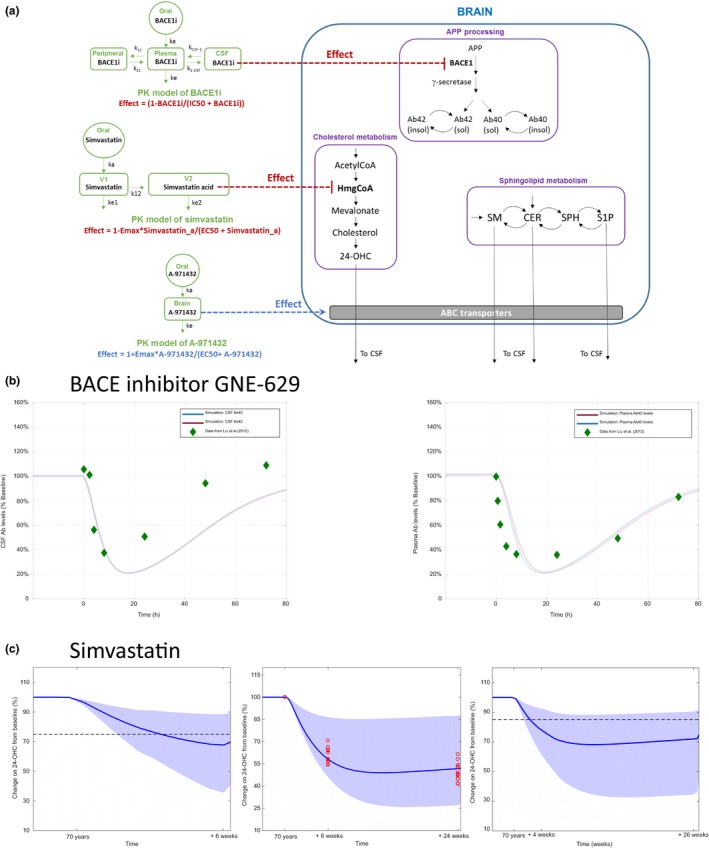
Validation of the quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) model using published data for therapies. (a) Schematic of the implementation of pharmacokinetic (PK) models for BACEi and simvastatin and their pharmacodynamic effect on BACE1 and HmgCoA in the brain compartment. The model for BACEi is based on the model proposed by ref. 23 and the model for simvastatin is based on the model proposed by ref. 24. (b) Bace inhibitor GNE‐629 (left) changes (% from baseline) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid beta (Aβ40) and Aβ42 levels from QSP model simulation and comparison with data reported by ref. 23. (Right) Changes (% from baseline) in plasma Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels from QSP model simulation and comparison with data reported by ref. 23. (c) Simvastatin. (Left) Comparison of simulations results with change in plasma 24‐OHC reported by ref. 25 after 6 weeks of treatment with a dose of 40 mg q.d. The mean response of the QSP model is just under 70% of the baseline value, which is close to the mean response reported (20–25% decrease of plasma levels of 24‐OHC from baseline). (Middle) Comparison of simulations results with change in plasma 24‐OHC reported by ref. 26 after 6 and 24 weeks of treatment (red points) with a dose of 80 mg q.d. of simvastatin. The mean response of the QSP model is around 35% decrease in 24‐OHC, in good agreement with the reported clinical dynamics of plasma 24‐OHC 26 (40–60% decrease of plasma 24‐OHC compared to baseline). (Right) Comparison of simulations results with change in CSF 24‐OHC reported by ref. 27 after 4 weeks of a dose of 40 mg q.d., followed by a dose of 80 mg q.d. for 22 weeks (red points). The mean response of the QSP model is around 30% decrease in CSF 24‐OHC levels, compared to a reported slight decrease of 8–15% in CSF 24‐OHC levels.27 APP, amyloid precursor protein; Cer, ceramide; EC50, half‐maximal effective concentration; Emax, maximum effect; IC50, half‐maximal inhibitory concentration; OHC, hydroxycholesterol; S1P, sphingosine‐1‐phosphate; SM, Sphingomyelin; SPH, Sphingosine.
