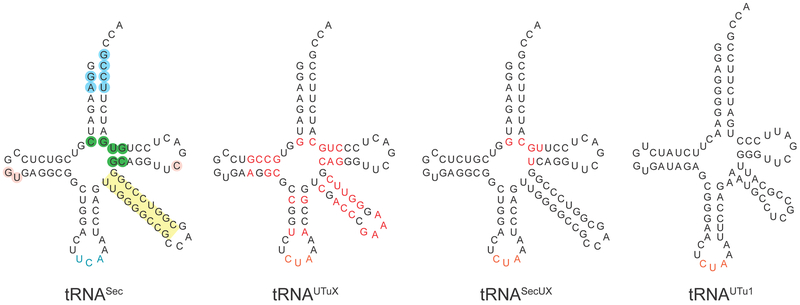
Figure 1.
Wild-type and synthetic selenocysteine tRNAs. Identity nucleotide determinants of wild-type E. coli tRNASec are shaded blue, and the variable arm, whose length and orientation are specifically recognized by SerRS, is highlighted in yellow. Nucleotides that govern the tertiary fold of tRNASec are given in pink. Base pairs acting as EF-Tu antideterminants are shown in green. Synthetic selenocysteine tRNAs employed in this study are given in black, except the amber anticodon (in purple). Mutations introduced into tRNAUTuX and tRNASecUX are indicated in red. tRNAUTu1, derived from a metagenome sequence [10,15] is too dissimilar to E. coli tRNASec to highlight nucleotide differences.