Figure 4.
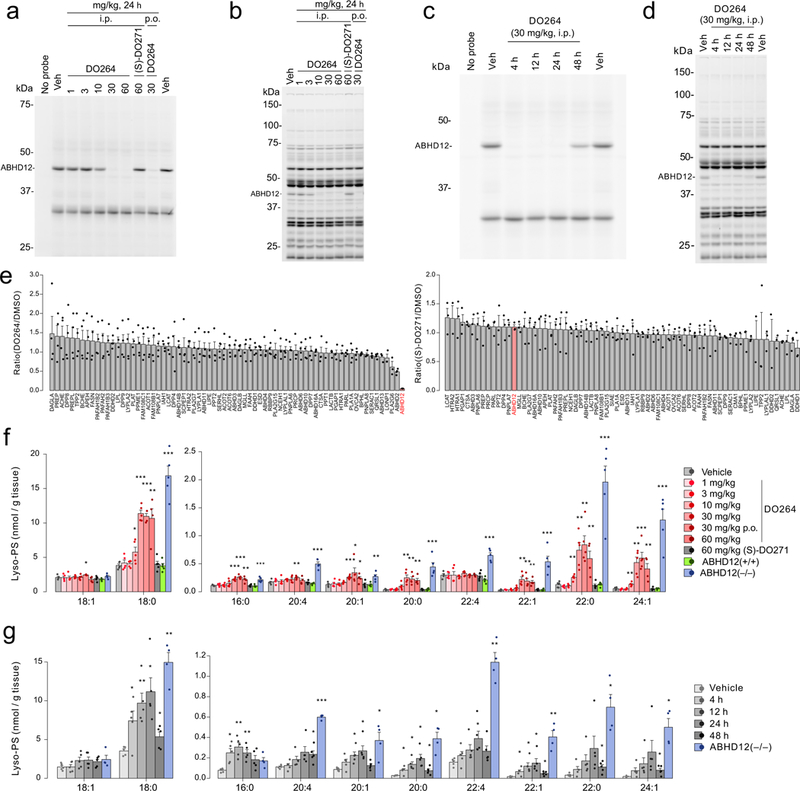
DO264 inhibits ABHD12 and increases brain lyso-PS content in vivo. (a, b) Dose-dependent inhibition of ABHD12 in mice treated with the indicated doses of DO264 (24 h, i.p.), as determined in brain membrane proteome by gel-based competitive ABPP using (a) the JJH350 probe (2 μM, 45 min, 37 °C) or (b) the FP-rhodamine probe (1 μM, 45 min, 37 °C). (c, d) Time-course analysis of inhibition of ABHD12 in DO264-treated mice (30 mg/kg, i.p., indicated time points) as determined in brain membrane proteome by gel-based competitive ABPP using (c) the JJH350 probe (2 μM, 45 min, 37 °C) or (d) the FP-rhodamine probe (1 μM, 45 min, 37 °C) (d). For a-d, the results are representative of two independent experiments. (e) Quantitative MS-ABPP of brain membrane serine hydrolase activities from mice treated with vehicle versus DO264 (left plot) or (S)-DO271 (right plot) (30 mg/kg compound, i.p., 4 h treatment). Data represent the mean of median ratios ± SEM for peptides quantified for each protein. n = 4 and 3 independent samples for DO264 and (S)-DO271 data, respectively. (f) Brain lyso-PS content from mice treated with vehicle or the indicated doses of DO264 or (S)-DO271 (i.p., 24 h, except where indicated p.o. for oral dosing groups). The lyso-PS content of brain tissue from ABHD12(+/+) and ABHD12(−/−) mice were included for comparison. (g) Time-course analysis of brain lyso-PS content from mice treated with vehicle or DO264 (30 mg/kg, i.p.). The lyso-PS content of brain tissue from ABHD12(−/−) mice was included for comparison. For f and g, data represent mean ± SEM. n = 5 mice per group except the ABHD12(−/−) mice group in g (n = 4 mice). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 (Two-sided Student’s t-test performed relative to vehicle-treated mice for f and g). The p-values and other lipid species measured for f and g are provided in Supplementary Table 4.
