FIGURE 2.
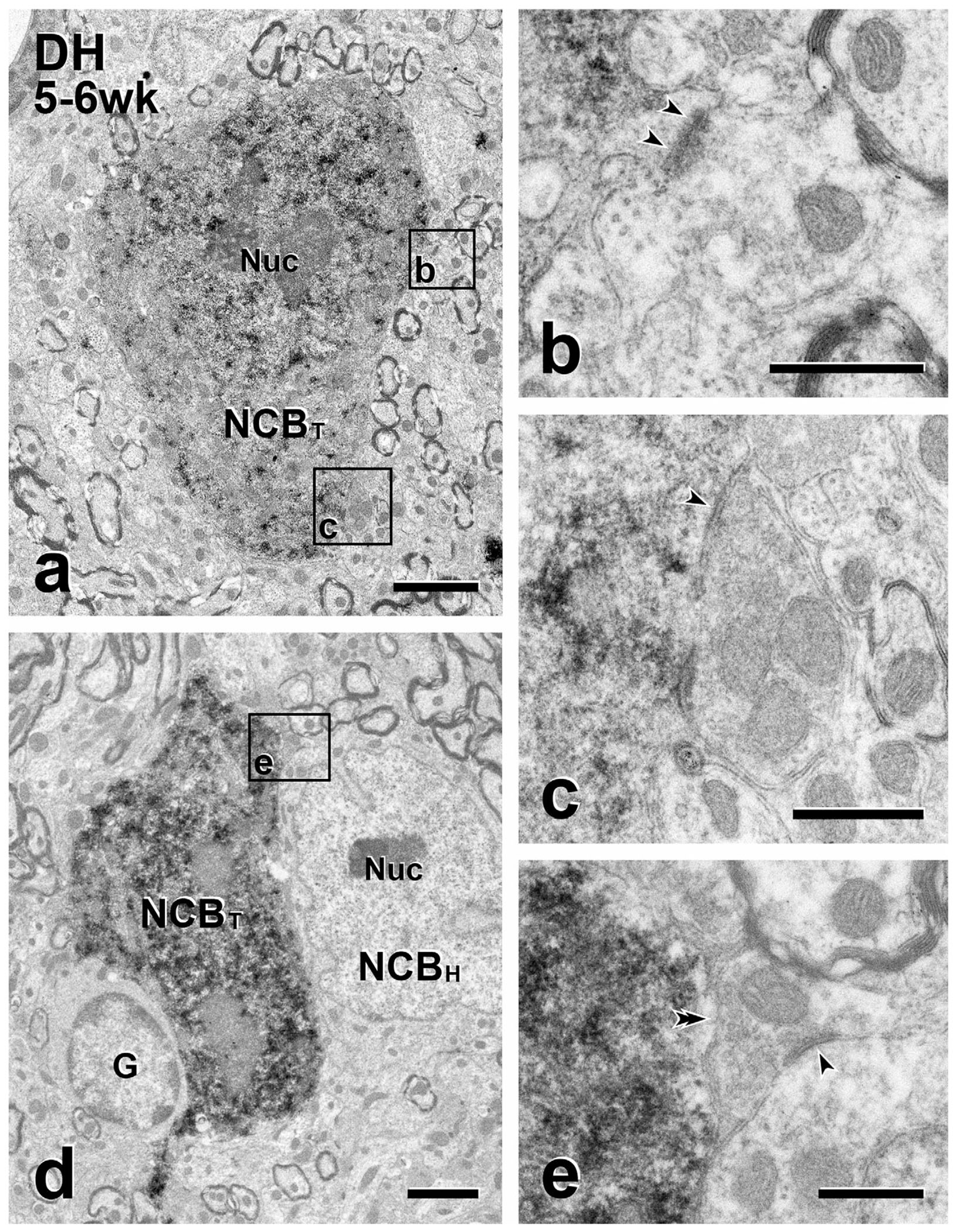
Short-term transplants: presynaptic inputs from the host to transplant cell bodies. (a & d) Immunoperoxidase reaction product identifies GFP-immunoreactive transplant cell bodies (NCBT) in the dorsal horn (DH). Boxed areas in (a) (Boxes b, c) and in (d) (Box e) illustrate unlabeled (host) axon terminals presynaptic (arrowheads) to GFP-labeled transplant cell bodies. In (a), the transplant cell body receives both an asymmetric and a symmetric synapse. The density postsynaptic to the unlabeled terminal in (b) is thick (i.e., an asymmetric synapse) whereas the density postsynaptic to the unlabeled terminal in (c) is thin (i.e., a symmetric synapse). In (d), the cell body of a GFP-negative (host) neuron (NCBH) and a glial cell (G) abut the GFP-positive transplanted cell body. (e) The unlabeled axon terminal in (e) directly contacts (double arrowhead) the GFP-positive cell body in (d), without an intervening glia process and also forms a symmetric synapse (arrowheads) with an unlabeled host cell body. Nuc, neuronal nucleus. Scale bars: 2 μm in (a, d); 500 nm in (b, c, e)
