FIGURE 9.
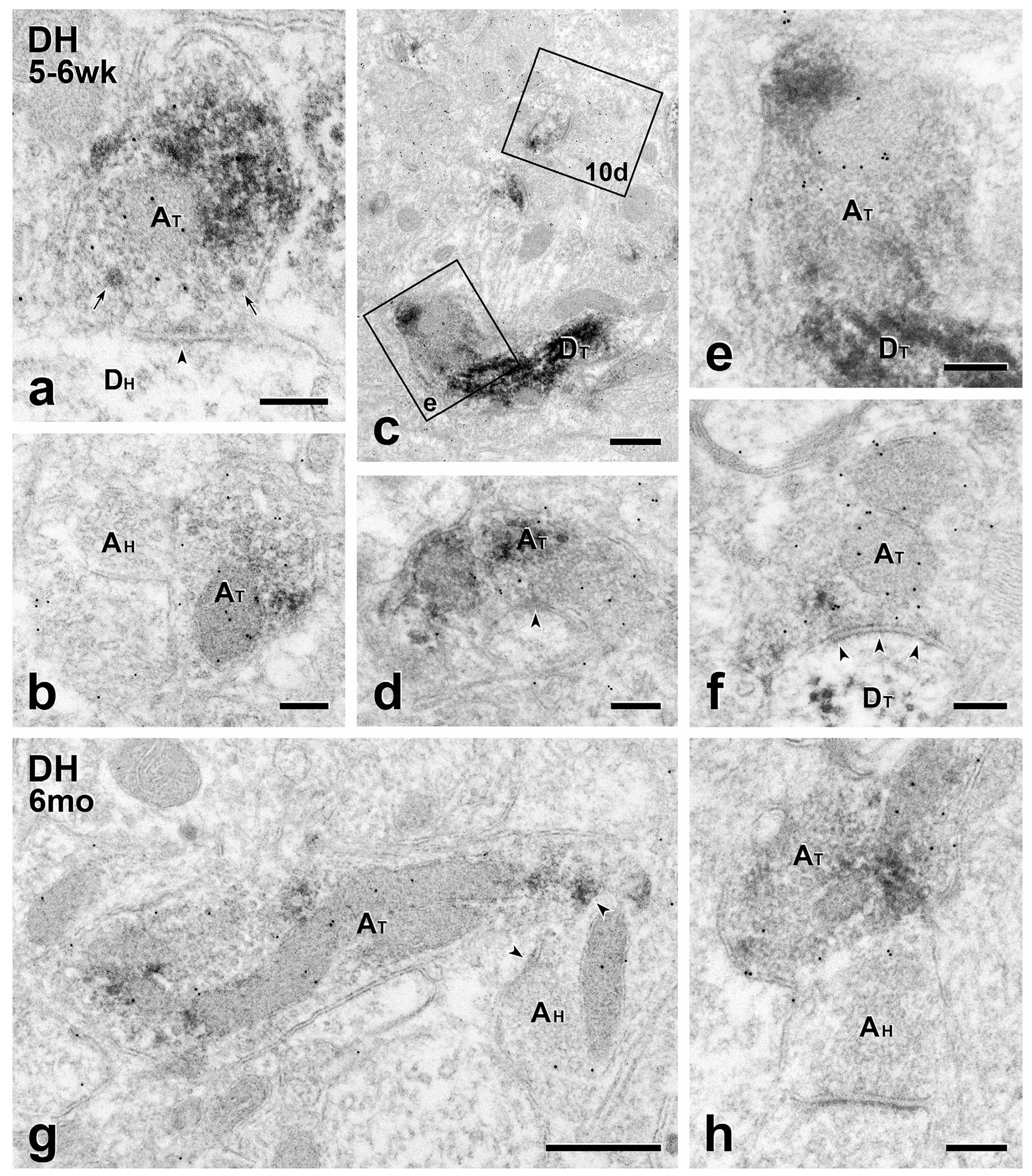
Short- and long-term transplants: MGE-derived axon terminals are GABA-immunoreactive. (a–f) Short term transplants. GABA immunolabeling of GFP-immunoreactive MGE-derived axon terminals (AT) with 10 nm gold illustrates the transmitter phenotype of transplant terminals and the breadth of the circuitry in which they engage. (a) A symmetric transplant-derived presynaptic input (arrowheads) to an unlabeled host dendrite (DH). Both small clear and large granular vesicles (arrows) occur in the transplant terminal. (b) Axoaxonic apposition between transplant (GFP- and GABA-positive; AT) and host-derived (GFP- and GABA-negative; AH) terminals. (c) 10nm gold-immunolabeled transplant-derived dendrites (DT). Boxed areas (e) and 10d are shown at higher magnification in Figures 9e and 10d, respectively. (d) Symmetric GABA-immunoreactive, transplant-derived (AT) presynaptic input (arrowhead) to a small, unlabeled host dendrite. (e) A GABA-gold labeled transplant-derived terminal (AT) directly contacts a transplant-derived dendrite (DT). (f) Transplant-derived (AT), GABA-immunoreactive symmetric input (arrowheads) to a transplant-derived dendrite (DT). (g & h) Long term transplants. Transplant-derived, GABA-immunoreactive terminals (AT) directly contact host axon terminals (AH). The latter are presynaptic to unlabeled host dendrites. Scale bars: 500 nm in (c) and (g); 200 nm in all others
