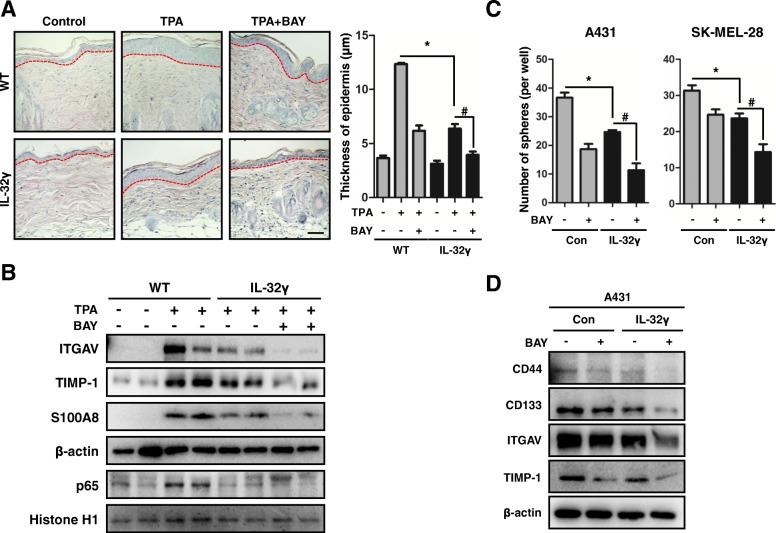
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of NF-κB activity suppresses cancer stemness and skin inflammation. a Effects of BAY on TPA-induced epidermal hyperplasia. WT and IL-32γ mice were topically administrated with BAY and TPA application and then sacrificed after 24 h. Dorsal skin tissues were analyzed by H&E staining. Representative images of skin tissues are shown. The bar graph shows the average epidermal thickness of mice in each group. Scale bar, 10 μm. n = 3. *p < 0.05; #p < 0.05. b Western blotting of ITGAV, TIMP-1 and S100A8 in cytosolic extracts and p65 in nuclear extracts of skin tissues from single TPA-treated with BAY mice are shown. c Effects of NF-κB inhibitor Bay 11–7082 (BAY) on skin cancer cell sphere formation. Control and IL-32γ-overexpressing A431 and SK-Mel-28 cells were subject to sphere assay in the presence of Bay (5 μM) for 10 days. d Expression of CD44, CD133, ITGAV and TIMP-1 in A431 CSCs. Control and IL-32γ-overexpressing A431 CSCs were treated with BAY (5 μM) for 24 h. Protein levels of CD44, CD133, ITGAV and TIMP-1 were detected by western blotting