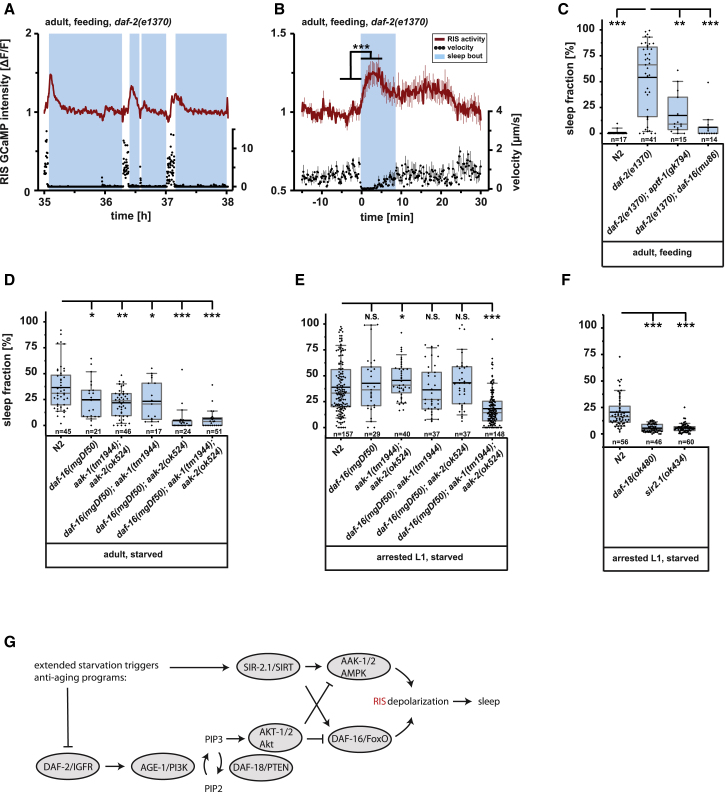
Figure 4.
The Nutrient-Sensing Longevity Regulators IIS and AMP Kinase Regulate Starvation Sleep through RIS Activation
(A) RIS GCaMP3 signal intensities and corresponding velocity traces of a representative daf-2(e1370) mutant worm. RIS activity is shown in red and locomotion speed in black; blue shading shows sleep bouts as defined by a locomotion cessation threshold. At the onset of a sleep bout, RIS activated and locomotion ceased. Note that RIS depolarizes at sleep onset and is not depolarized during the entire quiescence bout, which is similarly observed in the dauer larva.
(B) Averaged RIS activity and velocity aligned to sleep bout onset. RIS activity (ΔF/F) increased by 17.9% ± 4.7% during sleep (n = 15 worms; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; paired Wilcoxon rank test).
(C) DAF-2 inhibition induces sleep through RIS and DAF-16. Median sleep time was 66% in daf-2(e1370); 9% in daf-2(e1370); aptf-1(gk794), ∗∗p < 0.01; and 0% in daf-2(e1370); daf-16(mu86), ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) Longevity genes control starvation-induced sleep in the adult: median time spent in sleep was 31% in wild-type; 24% in daf-16(mgDf50) mutation, ∗p < 0.05; 24% in aak-1(tm1944);aak-2(ok524) double mutants, ∗∗p < 0.01; 21% in daf-16(mgDf50)/aak-1(tm1944) double mutants, ∗p < 0.05; 0% in daf-16(mgDf50)/aak-2(ok524) double mutants, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; and 4% in daf-16(mgDf50)/aak-1(tm1944)/aak-2(ok524) triple mutants, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(E) Longevity genes control starvation-induced larval sleep. Single or double mutation combinations did not reduce sleep significantly, but, compared with wild-type (median sleep fraction 33%), the daf-16(mgDf50)/aak-1(tm1944)/aak-2(ok524) triple mutant reduced sleep (median sleep fraction 14%); ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(F) Insulin signaling and sirtuin, which control the activity of FoxO and AMPK, control sleep. Median sleep fraction was 16% in wild-type; 4% in daf-18(ok480), ∗∗∗p < 0.001; and 5% in sir-2.1(ok434), ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(G) Hypothetical working model that integrates literature data with our observations. The numbers of assayed worms (n) are displayed below the boxplots. Sleep duration comparisons with N2 were made using the Mann-Whitney U test and were confirmed with Benjamini-Hochberg procedure for multiple comparisons. Error bars indicate the SEM.
See also Figure S4 for tissue-specific rescue experiments.