Figure 3.
Expression of lncRNAs Is Correlated with Neighboring PCGs
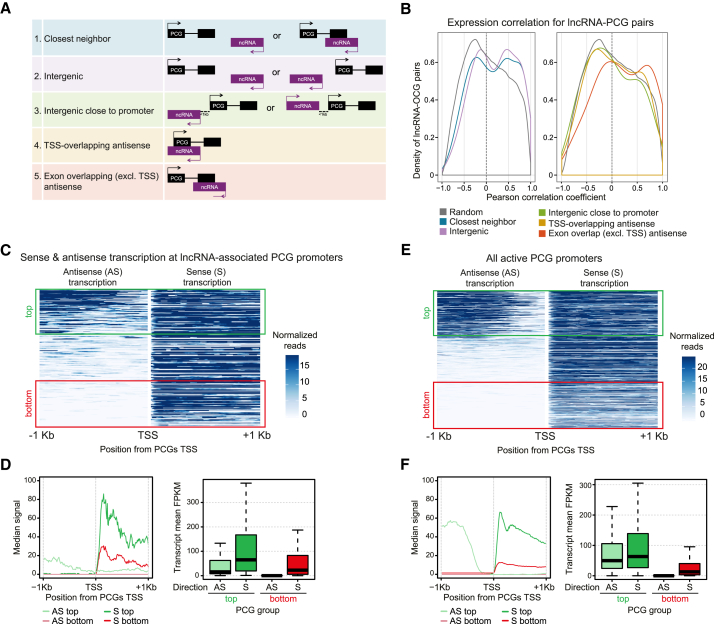
(A) Schematic showing different lncRNA-PCG (protein coding gene) pair sets.
(B) Distribution of expression correlations between lncRNAs and their paired PCGs in each group (defined in A). Correlation coefficients calculated using expression levels across each individual sample are shown. Background set composed of 349,000 randomly associated lncRNA-PCG pairs (gray line) is shown.
(C) Sense and antisense (divergent) transcription around lncRNA-associated PCG promoters. PCGs involved in lncRNA-PCG antisense pairs considered from all groups (A) are shown: 501 lncRNA-PCG antisense pairs. Heatmap shows mesodermal RNA-seq (3–4 hr) counts of divergent transcripts (10-bp windows, across 2 kbp regions) centered on the TSS of annotated mesoderm-expressed PCG genes, in either antisense (left) or sense (right) direction. Transcripts ordered based on levels of antisense expression (divergent transcription) are shown. Top (green) and bottom (red) thirds of divergent expression are boxed.
(D) (Left) Median values of sense and antisense transcription for top and bottom groups. (Right) Genes with high (top third) divergent transcription have significantly higher expression levels than genes without (bottom third) divergent transcription (p = 8.659e−09; Wilcoxon test).
(E and F) Same as (C) and (D) but assessing promoters of all expressed PCGs (11,780 transcripts; STAR Methods). Again, genes with high (top third) divergent transcription have significantly higher expression levels than those with the low divergent transcription levels (p < 2.2e−16; Wilcoxon test; F).
See also Figure S7.