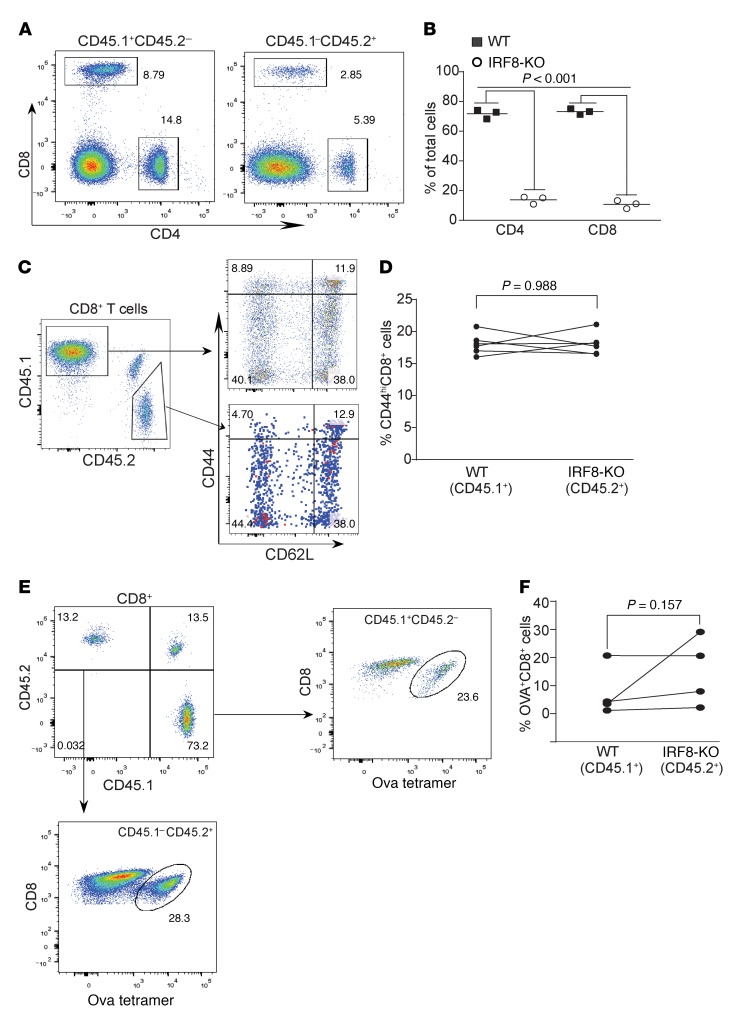
Figure 5. IRF8 regulates antigen-specific CD8+ T cell differentiation and activation in a cell-extrinsic manner.
(A) Competitive mixed BM chimeras were created by adoptively transferring SJL (CD45.1+) WT whole BM cells with Irf8–/– BM cells into lethally irradiated C57BL/6×SJL) F1 recipients (CD45.1+CD45.2+). Peripheral blood cells were collected from WT and IRF8-KO mixed BM chimera mice, stained with CD45.1-, CD45.2-, CD4-, and CD8-specific mAbs, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Shown are representative plots of phenotypes of WT (CD45.1) and IRF8-KO (CD45.2) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the mixed BM chimeras. (B) The CD4+ and CD8+ cells from WT (CD45.1) and IRF8-KO (CD45.2) as shown in A were quantified. (C) Blood cells from WT and IRF8-KO mixed BM chimera mice were stained with CD45.1-, CD45.2-, CD8, CD44-, and CD62L-specific mAbs. CD8+ T cells were gated out for CD45.1 and CD45.2 cells. The WT and IRF8-KO CD8+ cells were then analyzed for CD44hi and CD62L+ cells. Representative plots of 1 of 3 mice are shown. (D) The percentage of CD44hi cells of the WT CD8+ and IRF8-KO CD8+ T cells was quantified. (E) WT (CD45.1) and IRF8-KO (CD45.2) mixed BM chimera mice were vaccinated with OVA peptide, followed by a boost with OVA peptide 14 days later. Peripheral blood was collected 7 days after boost and stained with MHCII-, CD8-, and OVA tetramer–specific antibodies. MHCII-CD8+ cells were gated for OVA tetramer+ cells. Shown are representative plots of OVA-specific WT and IRF8-KO CD8+ T cells. (F) The WT and IRF8-KO CD8+ OVA-specific T cells as shown in E were quantified.