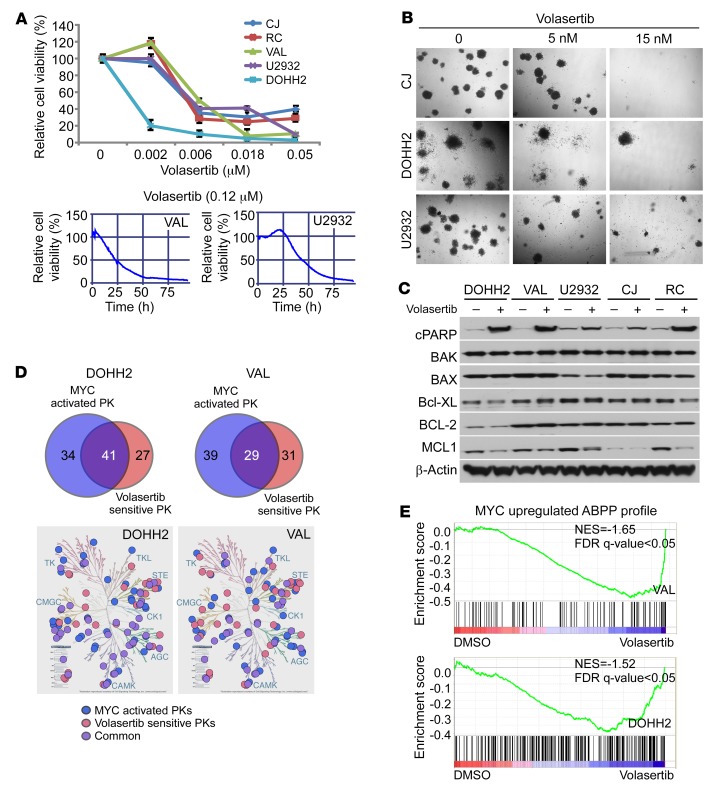
Figure 5. PLK1 function is required for the maintenance of DHL.
(A) Volasertib treatment compromises DHL cell survival. Dose response and time course of volasertib treatment on cell viability of DHL and BL cells, as indicated by percentage of cell viability, as determined by cell titer blue assays (upper panel) and imaging-based drug screening assay (lower panels). (B) Volasertib treatment inhibits the clonogenic capacity of DHL cells seeded in methylcellulose. Original magnification, ×40. (C) Volasertib treatment (20 nM for 24 hours) provokes the cleavage of PARP and suppresses MCL-1 protein levels in DHL cells. Western blot analysis of the indicated cells was performed to assess the effects of PLK1 inhibition on the expression of BCL-2 family members. (D) Overlap of MYC-upregulated kinases and PLK1-dependent kinases in DOHH2 and VAL DHL cells. MYC-activated protein kinases (PK) were determined by ABPP after CRISPR/cas9-mediated MYC KO/KD in DHL lines DOHH2 and VAL cells (versus parental cells) and PLK1-senstive protein kinases were determined after 2 hours of volasertib treatment (20 nM) in DOHH2 and VAL cells. log2 fold change of more than 1 indicates increased kinase ATP probe binding with relative increased activity, and log2 fold change of –1 or less indicates decreased ATP probe binding with decreased activity relative to parental cells. Data presented are the average of 3 biological replicates performed in duplicate. Kinome tree illustration reproduced courtesy of Cell Signaling Technology (www.cellsignal.com). (E) GSEA of the MYC-activated ABPP profile (upper panel) and of the ABPP profile changes provoked by PLK1 inhibition (lower panel) establish that volasertib treatment represses MYC-activated kinases (from DOHH2 and VAL MYC-KO ABPP profile). Normalized enrichment score (NES) = –1.65 (VAL); NES = –1.52 (DOHH2). Data shown in B and C are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. See complete unedited blots in the supplemental material.