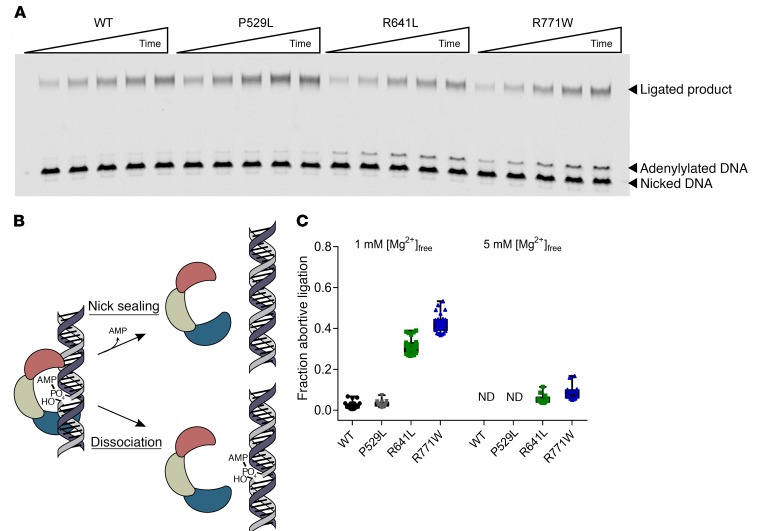
Figure 7. R641L and R771W LIG1 mutants generate abortive ligation intermediates at physiological Mg2+ concentration.
(A) Representative denaturing polyacrylamide gel analyzing multiple-turnover ligation with 5 nM LIG1, 500 nM DNA, and 1 mM free Mg2+. (B) Schematic for abortive ligation by LIG1. After catalyzing adenylyl transfer, LIG1 can either catalyze the nick-sealing step or dissociate from the adenylylated DNA intermediate. (C) Fraction abortive ligation was calculated for WT and mutant enzymes at both 1 mM and 5 mM free Mg2+ (mean ± SD; n ≥ 3). ND, not detected. See Supplemental Figure 5 for the initial rates for formation of ligated product and adenylated DNA.