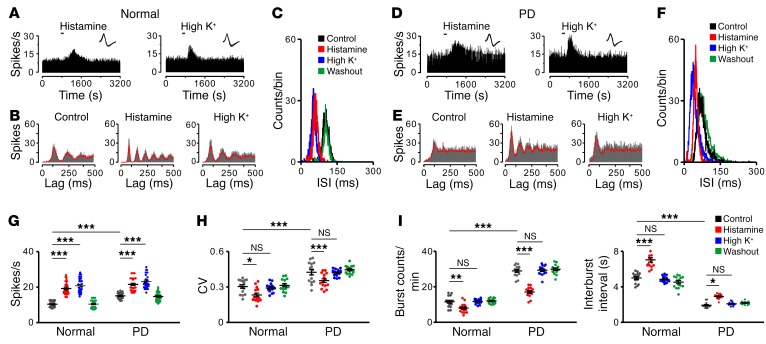
Figure 2. The histamine-induced regularization of firing patterns of STN neurons in normal and PD rats.
(A–F) Effects of histamine (1 μg) and high K+ (0.75 μg KCl) on firing rate and firing pattern of 2 recorded STN neurons in normal and PD rats in vivo. PSTHs (A and D) show that both histamine and high K+ excited the STN neuron. Insets represent 5 superimposed traces of spike waveforms for each unit, respectively. Autocorrelation histograms (B and E) show that histamine, rather than high K+, promoted periodicity of STN neuronal firing. ISI histograms (C and F) show that histamine, but not high K+, narrowed ISI distributions. (G–I) Histamine increased firing rates (G, n = 30), decreased CV of ISIs (H, n = 15), reduced number of bursts (I, left panel, n = 15), and prolonged the interburst intervals (I, right panel, n = 15) of STN neurons in both normal and PD rats. However, high K+ only increased firing rates (G), but did not influence firing patterns (H and I) of STN neurons in normal and PD rats. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, 2-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post hoc test (G–I).