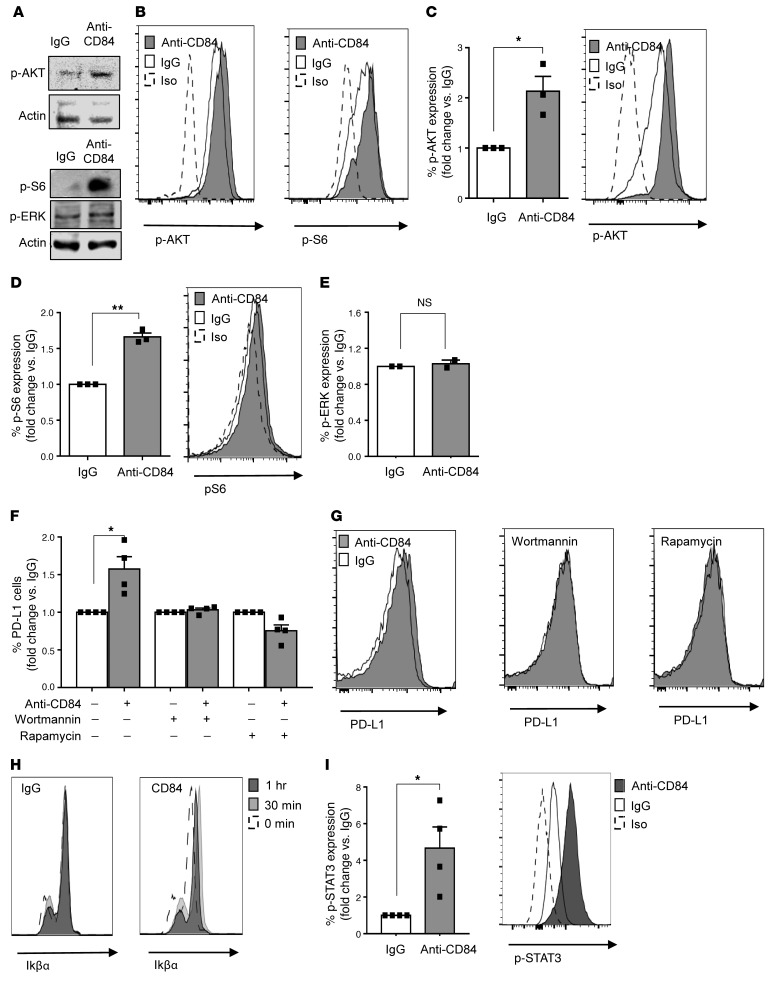
Figure 2. Activation of cell-surface CD84 elevates PD-L1 levels through the p-AKT/mTOR pathway.
(A and B) M210B4 cells (1 × 105) were stimulated with anti-CD84 (4 μg/ml) for 15 minutes, followed by anti-FAB cross-linking for 5 minutes. (A) Cells were lysed, and lysates were separated on 12% (wt/vol) SDS-PAGE and blotted with anti–p-S6, anti–p-AKT, anti–p-ERK, or actin. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and subsequently stained with anti–p-AKT and anti–p-S6 antibodies followed by a secondary anti-rabbit allophycocyanin-conjugated (APC-conjugated) antibody. Histograms are representative of 2 independent experiments. (C–E) Primary CLL cells were stimulated with control (IgG) or anti-CD84–activating (5 μg/ml) antibodies for 5 minutes, followed by anti-FAB cross-linking for an additional 5 minutes. Then, the cells were fixed, and p-ERK, p-AKT, and p-S6 levels were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 3; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, 2-tailed, paired t test). (F and G) CLL cells were incubated with the inhibitors wortmannin and rapamycin (0.1 μM) for 20 minutes. The cells were then stimulated with anti-CD84–activating (5 μg/ml) antibodies, or IgG control. After 48 hours, the cells were analyzed by FACS for PD-L1 cell-surface expression (n = 4; *P < 0.05, 2-tailed, paired t test). (H and I) CLL cells were stimulated with IgG or anti-CD84–activating (5 μg/ml) antibodies for 0, 15, and 30 minutes, followed by anti-FAB cross-linking for 0, 15, and 30 minutes. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with IkBα (n = 2) (H), or p-STAT3 (n = 4) (I) antibodies. *P < 0.05, 2-tailed, paired t test.