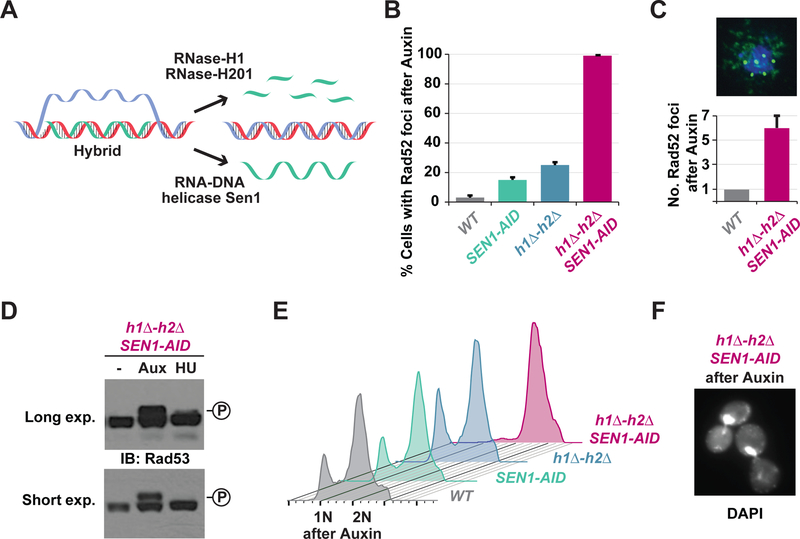
Fig. 1. Blocking the R-loop removing enzymes causes high levels of irreparable DNA damage and cell-cycle arrest.
(A) Cartoon of hybrid removal pathways. RNase-H1 and RNase-H2 degrade the RNA while Sen1 helicase unwinds hybrids. (B) DNA damage in cells with persistent hybrids. Asynchronous cultures of wild-type (WT), auxin-inducible degron allele of Sen1 (SEN1-AID), deletion alleles of RNase-H1 and RNase-H2 (h1Δ-h2Δ), or both (h1Δ-h2Δ SEN1-AID) were treated with auxin for 4h and then scored for Rad52-GFP foci. (C) Asynchronous cultures of WT and h1Δ-h2Δ SEN1-AID were treated with auxin for 4h and then prepared for chromosome spreads using an antibody against endogenous Rad52 (green), the DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Quantification of 100 cells is shown with bar graph. (D) Rad53-phosphorylation in cells with persistent hybrids. Asynchronous cultures of h1Δ-h2Δ SEN1-AID cells were untreated (-), treated for 4h with auxin (Aux) or 2h with hydroxyurea (HU). Western-blot was performed using Rad53 antibody. The levels of phosphorylated-Rad53 (upper band) were significantly greater when cells were treated with auxin compared to HU. (E) DNA content in cells with persistent hybrids. Cultures in (B) were analyzed by FACS to assess DNA content. Only the h1Δ-h2Δ SEN1-AIDculture arrested in G2/M (2N). (F) Cell morphology of h1Δ-h2Δ SEN1-AIDtreated with auxin for 4h. DNA was stained with DAPI. Cells presented a large budded morphology typical of G2/M arrested cells.