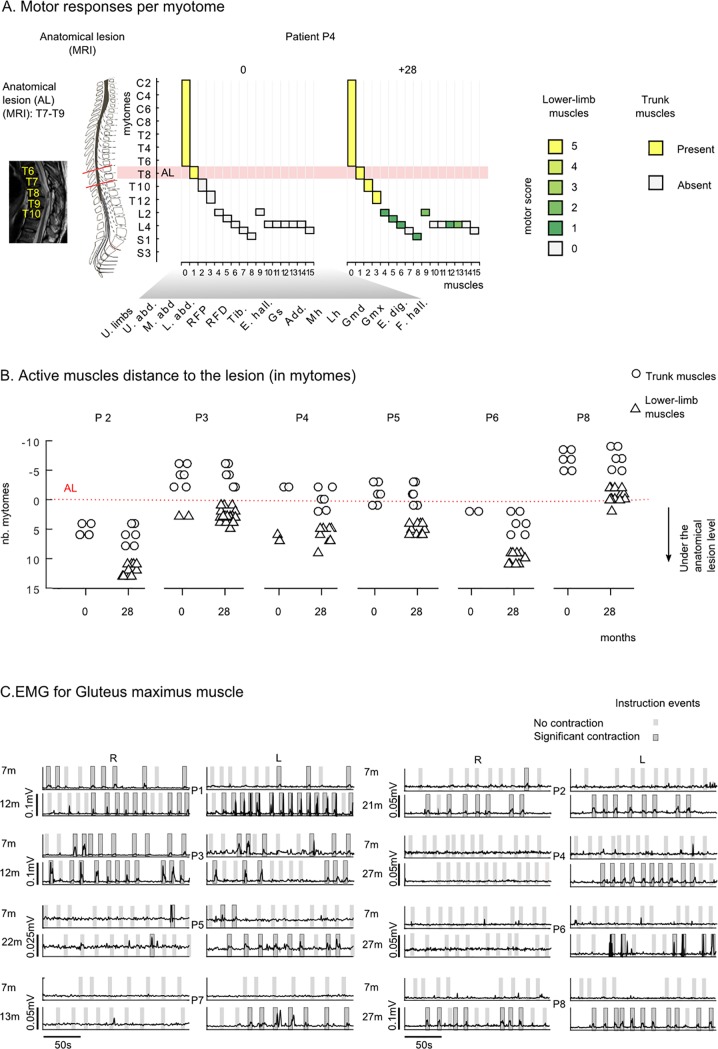
Fig 5. Motor improvement.
Neurological and neurophysiological evidence. (A) Example of active myotomes compared to the Anatomical Lesion (AL) shown for patient P4. For each muscle, the graphic shows the corresponding myotome level (considering the principal nerve root, S2 Table), and the clinical score at the onset (0) and the end (+28 months) of the WARN training. The MRI of this patient’s spinal cord revealed an AL extending between T7 and T9 segments. Accordingly, at the onset of the training, the patient had preserved motor functions in the upper-limbs and the upper abdomen muscle (spinal nerve roots are located at T7-T8 level), but could not contract the middle and lower abdomen muscles (T9-T12 segment) nor any of the lower limb muscles. After 28 months of the WANR training, this patient had recovered partial motor functions in the middle and lower abdomen as well as in multiple lower limb muscle innervated under the AL, namely, rectus femoris proximal (L2) and distal (L3), hip adductor (L2), gluteus medius/maximus, tibialis anterior (L4), and gastrocnemius (S1). B) For each patient, we considered the muscles where motor functions were clinically observed (ASIA motor score = >1) and calculated the distance to the AL. The distance was calculated as the number of myotomes between the spinal nerve root of the muscle and the lowest segment of the AL. A positive value in the graph, corresponds to a muscle that is rooted below the anatomical lesion; and negative values refer to muscles rooted above the lesion. We report results for the onset (0) and the end of the training (28). Trunk muscles are reported with an open circle, lower limb muscles with an open triangle and upper limb muscles are not considered. (C) EMG envelops for the gluteus maximums muscle for all patients. Patients were instructed to contract their legs for periods of 5 seconds over a 3-minute period. Verbal instructions were given to the patient by the PT; and instruction periods are shown in gray in the graph. A dark gray area highlights the trials where the patient had a significant GMx contraction (> mean + 3xSD of the baseline), and light gray indicates those where the contraction did not reach significance. Muscle responses are shown for all patients (P1 to P8) at an early stage and later in training.