Figure 6. ILC2 expression of CD73 is involved in ILC2-mediated suppression of NK cells.
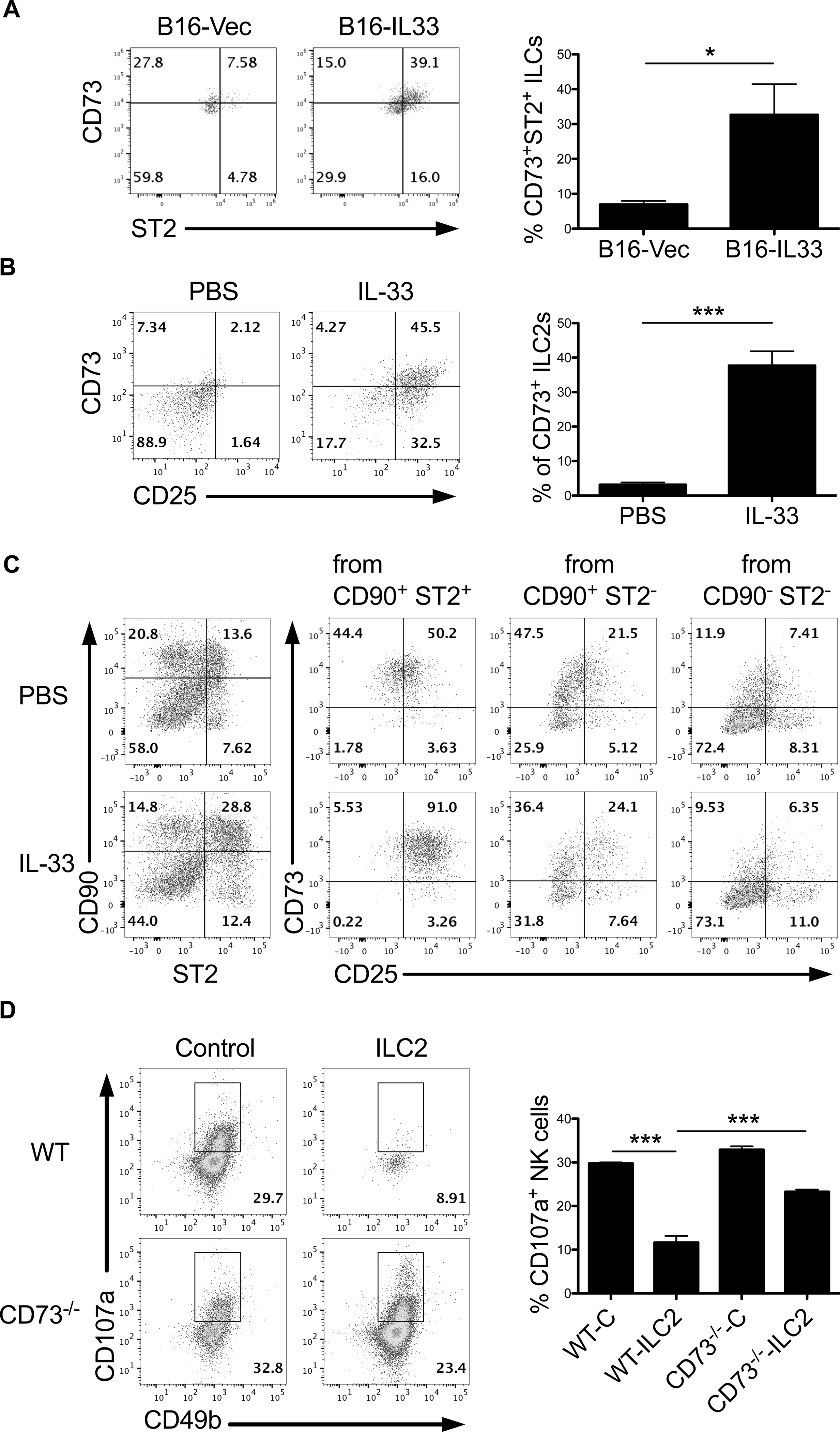
(A) Evaluation of ST2 and CD73 expression by intratumoral ILC2s from B16-Vec or B16-IL33 tumor-bearing Rag1−/− mice (n=4 mice per group). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of CD73 expression on activated splenic CD25+ ILC2 from PBS and IL-33-treated tumor-bearing Rag1−/− mice (n=4 mice per group). (C) Enriched splenic CD90+ ILCs from Rag1−/− mice were stimulated by PBS or recombinant IL-33 for 24h in vitro, and expression of CD73 and ST2 on CD90+ ILCs was determined by flow cytometry (left). Expression of CD73 and CD25 was further measured among ST2+CD90+, ST2-CD90+ and ST2-CD90- subsets (right). (D) CD107a expression among NK cells in coculture with WT or CD73−/− ILC2s. Control samples included BM cells cultured without IL-33 to serve as “control” ILC2s. ILC2s and NK cells were cocultured at a 1:1 ratio in 50μM AMP and 10ng/ml IL-33. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P< 0.05, *** P<0.001 as determined using a Student’s t-test.
