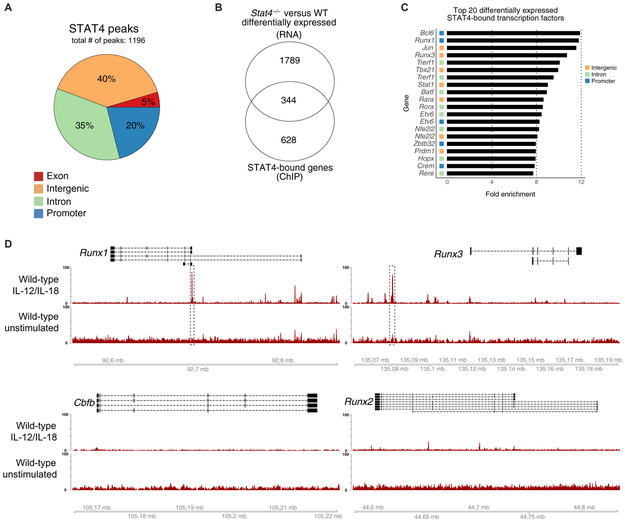
Fig. 1. STAT4 directly targets Runx transcription factors in activated NK cells.
Splenic NK cells (TCRβ−CD19−CD3ε−Ly6G−TER119−TCRγδ−NK1.1+) were sorted from WT mice and stimulated with IL-12 and IL-18 or media alone as a control (unstimulated). STAT4 ChIP was performed, followed by high-throughput DNA sequencing. (A) Proportions of STAT4 genome-wide occupancy at promoter (2 kb upstream and 0.5 kb downstream from TSS), intronic, exonic, or distal intergenic regions in cytokine-stimulated NK cells are shown. (B) RNA-seq was performed on splenic Ly49H+ WT NK cells and Stat4−/− NK cells sorted from mixed chimeras 2 days after MCMV infection. Venn diagram of overlap between differentially expressed genes (top; Padj < 0.05) identified through RNA-seq and reproducible STAT4-bound regions identified through ChIP-seq (bottom; IDR < 0.05). RNA-seq data were performed on n = 3 per condition. (C) Bar graphs depict the top 20 genes with greatest fold enrichment of STAT4 binding over input calculated by MACS2 in transcription factors that show differential expression in RNA-seq data. (D) Representative gene tracks for indicated core-binding factors from STAT4 ChIP-seq. ChIP-seq data are representative of three independent experiments with n = 15 to 20 pooled mice per group per experiment.