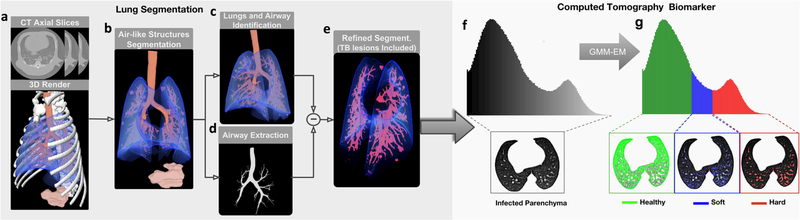
Fig. 1.
Lung Segmentation. From a the chest CT scan, b all aerated regions are identified. c The lungs, including the airways, are isolated successively by exploiting topological information. d Next, the airways tree is removed from the lungs. e Finally, to include the non-segmented damaged tissue, the lung segmentation is refined using a hole-filling method based on active contours. CT Biomarkers: The segmented lung volume is classified based on f the gray-level distribution in g three TB-associated tissue volumes: healthy, soft diseased, and hard diseased. Note: GMM-EM (Gaussian mixture model–Expectation maximization algorithm).