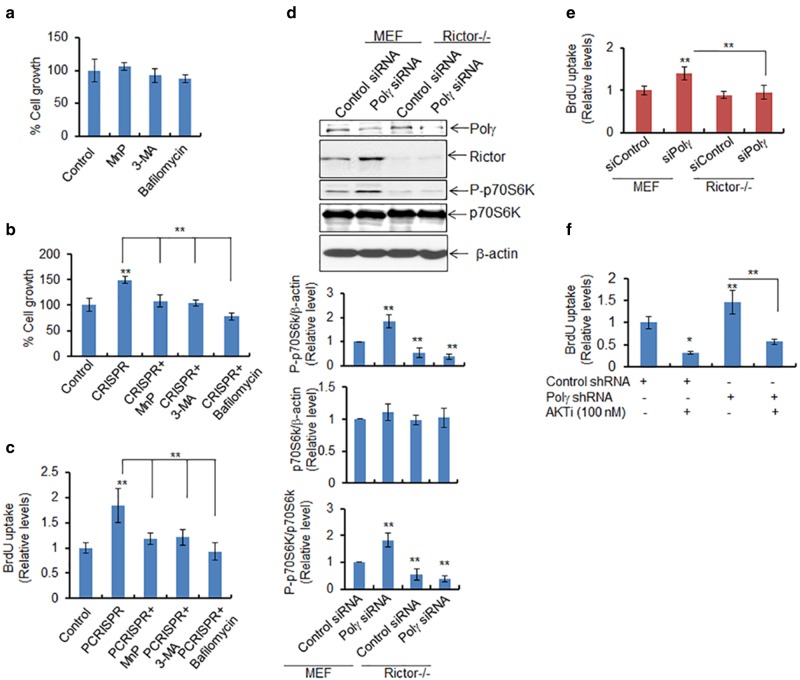
Fig. 7.
Deficiency of Polγ enhances autophagy-dependent cell proliferation. a The cytotoxicity of ROS and autophagy inhibitors (MnP, 20 μM; 3-MA, 2.5 mM; and Bafilomycin, 50 nM) was assessed in JB6 cells 24 h after treatment by determining cell growth. b Cell growth was also measured in PCRISPR cells following treatment with the indicated inhibitor. c BrdU uptake was determined as a measure of cell proliferation in PCRISPR cells with or without ROS or autophagy inhibitors. d Phosphorylation of p70S6K was detected by western blotting in wild-type and Rictor-knockout MEF cells following suppression of Polγ by siRNA. e Cell proliferation was determined in Rictor-knockout cells after Polγ suppression using the BrdU uptake assay (assay details are given in Materials and Methods section). f Cell proliferation was also determined in Polγ-knockdown cells following treatment with AKT inhibitor using the BrdU uptake assay. In all panels, each data point represents the mean ± SD of three individual samples. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA analysis and Bonferroni’s post-test for multiple-group comparisons. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks: *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01