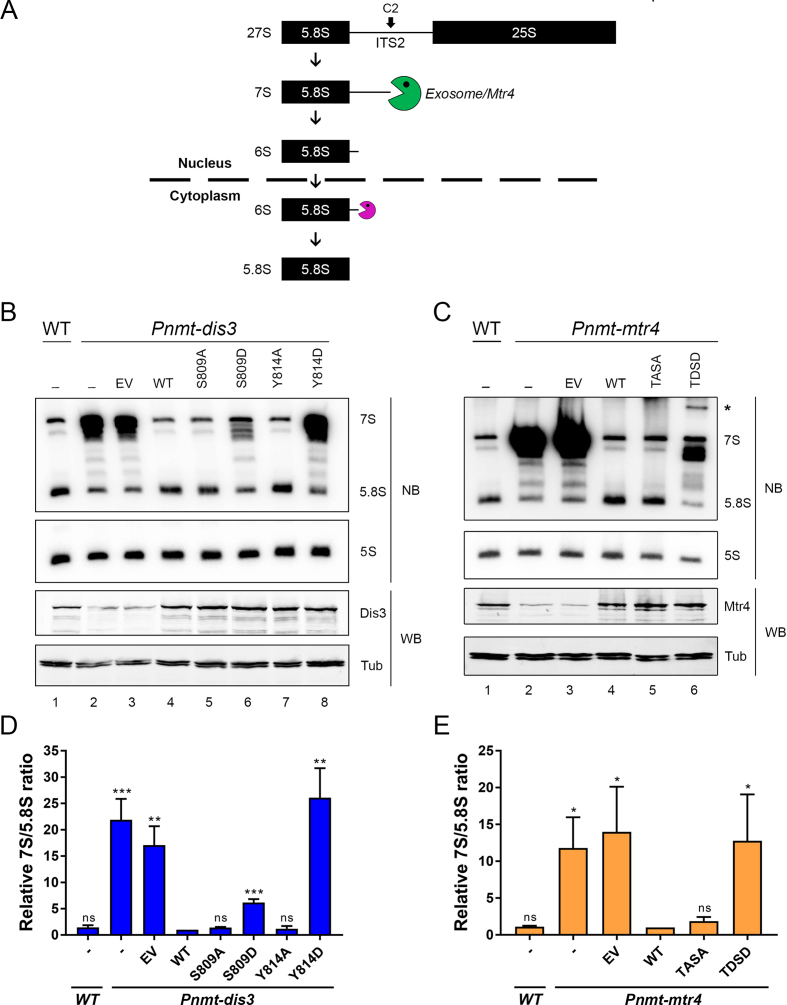
Figure 4.
Phospho-mimetic versions of Dis3 and Mtr4 result in defective 5.8S rRNA synthesis. (A) Schematic of 7S pre-rRNA processing into mature 5.8S rRNA. Following endonucleolytic cleavage of the 27S rRNA precursor at site C2, the 7S pre-rRNA is trimmed 3′-5′ by the nuclear exosome assisted by the helicase activity of Mtr4 (green pacman). The resulting 6S intermediate is further processed by cytoplasmic ribonucleases (purple pacman) to generate the mature 5.8S rRNA. (B) Western blot (WB) and Northern blot (NB) analysis of wild-type (lane 1) and Pnmt-dis3 (lane 2–8) strains expressing the indicated phospho-deficient (lanes 5 and 7) and phospho-mimetic (lanes 6 and 8) versions of Dis3. EV, empty vector control. The position of the 7S pre-rRNA and 5.8S rRNA are indicated on the right. (C) Western blot (WB) and Northern blot (NB) analysis of wild-type (lane 1) and Pnmt-mtr4 (lane 2–6) strains expressing the indicated phospho-deficient (TASA; lane 5) and phospho-mimetic (TDSD; lane 6) versions of Mtr4. EV, empty vector control. The position of the 7S pre-rRNA and 5.8S rRNA are indicated on the right. The asterisk (*) shows the 5′-extended product specifically detected in the phospho-mimetic version of Mtr4. (B-C) The 5S rRNA and Tubulin were used as loading controls for northern and Western blots, respectively. (D and E) Quantification of 7S/5.8S ratios for the indicated versions of Dis3 (D) and Mtr4 (E). The calculated 7S/5.8S ratio was normalized to the 5S rRNA and expressed relative to Pnmt-dis3 (D) and Pnmt-mtr4 (E) strains complemented with the wild-type version of Dis3 and Mtr4, respectively. (B–E) Pnmt-dis3 and Pnmt-mtr4 strains were cultured in thiamine-supplemented medium to deplete endogenous Dis3 and Mtr4, respectively. The data and error bars represent the average and standard deviation from at least three independent experiments. P-values * ≤0.05, ** ≤0.01, *** ≤0.001; Student's t-test.