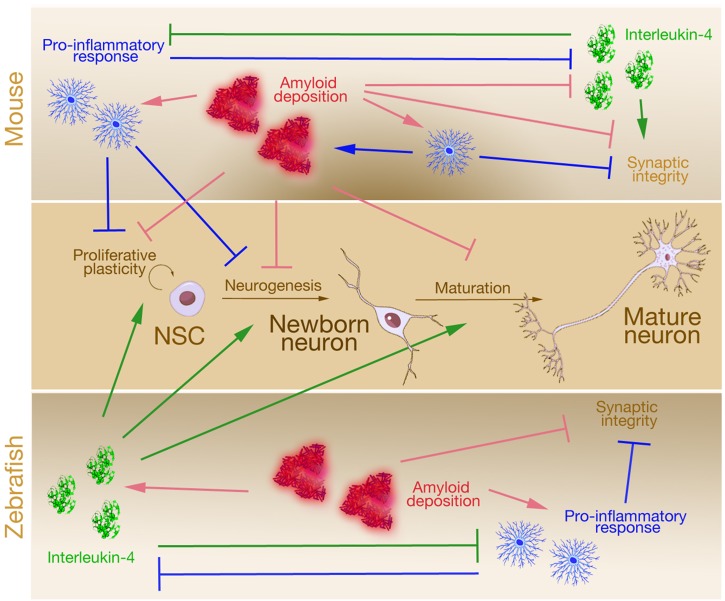
FIGURE 1.
A simplified comparison of the effects of Alzheimer’s disease on neural stem cell plasticity in mouse and zebrafish. In mouse, Amyloid deposition initiates pro-inflammatory response that potentiates Amyloid toxicity that impairs neural stem cell proliferation, neurogenesis, neuronal maturation, and synaptic integrity. This chronic inflammation suppresses anti-inflammatory factor Interleukin-4, which is beneficial for neuronal survival and synaptic integrity. In zebrafish, although Amyloid deposition follows a toxicity cascade similar to that of the mouse (activation of pro-inflammatory response and hampered synaptic integrity), Amyloid also leads to induction of anti-inflammatory factor Interleukin-4, which enhances neural stem cell proliferation, neurogenesis, and neuronal maturation. The effects of Interleukin-4 counteracts synaptic degeneration and reduced neural stem cell plasticity.