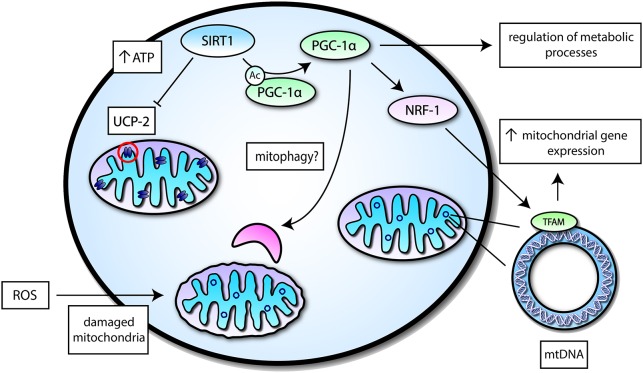
Figure 2.
A simplified overview of mitochondrial functions mediated by SIRT1 activity. SIRT1 may interact with transcription factors or mitochondrial proteins to induce different effects related to mitochondrial function—a select few of these proteins are highlighted. SIRT1 can suppress Uncoupling protein 2 (UCP-2) in the inner mitochondrial membrane to increase levels of ATP, which is important for energy metabolism. SIRT1 may also deacetylate Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) to induce its activation and augment mitochondrial biogenesis by increasing mitochondrial gene expression via Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1) and Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). PGC-1α itself can regulate different metabolic processes and may potentially play a role in mitophagy.