Figure 2. Morphology of the brain barriers illustrated in Fig. 1 .
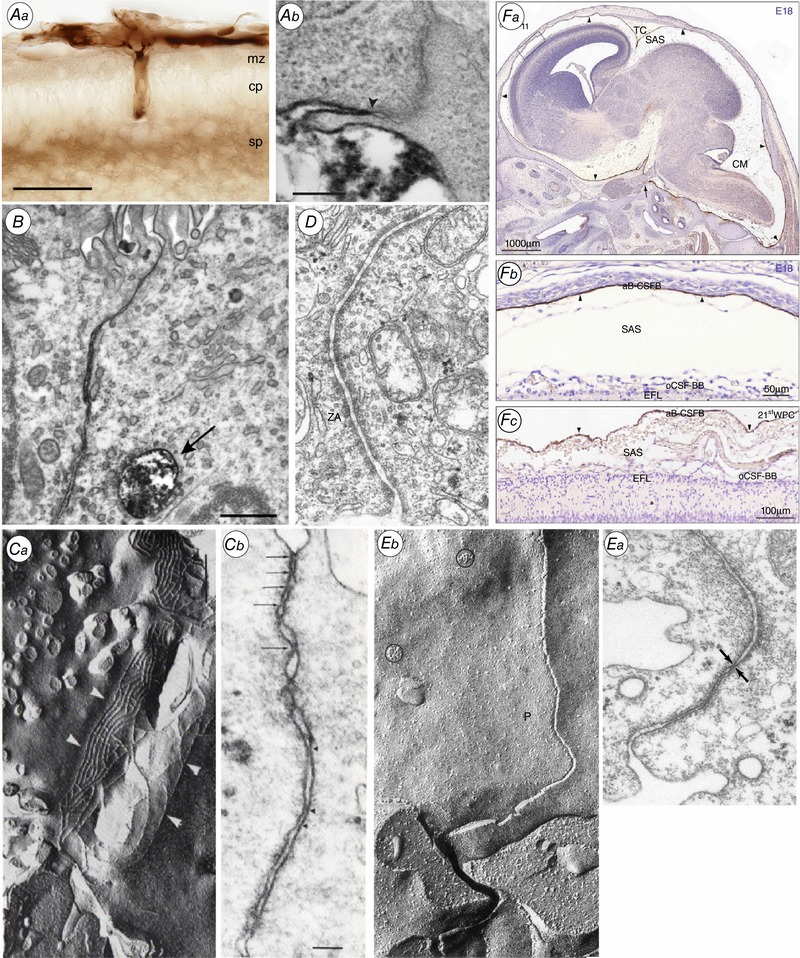
Aa, the blood–brain barrier. Light micrograph showing the localization of biotin ethylenediamine (BED) in the neocortex of opossum at P5 20–25 min after an intraperitoneal injection. Note that the staining for BED is most visible within the vessels, in the marginal and subplate zones. cp, cortical plate; mz, marginal zone; sp, subplate. Ab, localization of biotin–dextran (BDA3000) in the neocortex of P2 opossum 20–25 min after an intraperitoneal injection. Arrowhead points to site of the tight junction. Note that the marker is prevented from passing through the intercellular space by the tight junction. From Ek et al. (2006). B, the blood–CSF barrier. Lateral ventricular choroid plexus (blood–CSF barrier) in P13 Monodelphis. Tight junction excludes entry of BDA3000 into CSF. Labelled dextran present in one large and several smaller endosomes. From Ek et al. (2003). C, Circumventricular organs. a, adjacent tanycytes facing the CSF in circumventricular organs are connected by an extensive network of apical tight junctional strands shown here by freeze fracture of the adult Mongolian gerbil subcommissural organ. b, a thin section electron micrograph of the same region in a neonatal animal shows multiple ‘kissing points’ (arrows) between neighbouring tanycytes indicating a complete occlusion of the paracellular pathway. From Madsen & Møllgård (1979). D, ependyma in adult brain. Junctional configuration in the ependymal layer of 125‐day sheep fetus similar to those found in mature ependyma. ZA, zonulae adherens. Note unobstructed intercellular space. E, the embryonic CSF–brain barrier. a, thin‐section electron micrograph of the neuroepithelial lining of the cerebral vesicle from an E19 sheep. The junctional zone exhibits very narrow intercellular clefts which at places seem to be totally occluded (arrows). This junctional configuration has been named ‘strap’ junction. b, characteristic freeze fracture single strand of strap junction perpendicular to CSF surface. From Møllgård et al. (1987). F, the meningeal barrier. Distribution of claudin‐11 immunoreactivity in sagittal sections of E18 rat (a and b) and 21st wpc human (c) brain. Demonstrates a strong reactivity of the entire arachnoid barrier cell layer = arachnoid blood–CSF barrier (aB‐CSFB, arrowheads). From Brøchner et al. (2015). CM, cisterna magna; EFL, radial glial end feet layer; SAS, subarachnoid space; TC, tentorium cerebelli.
