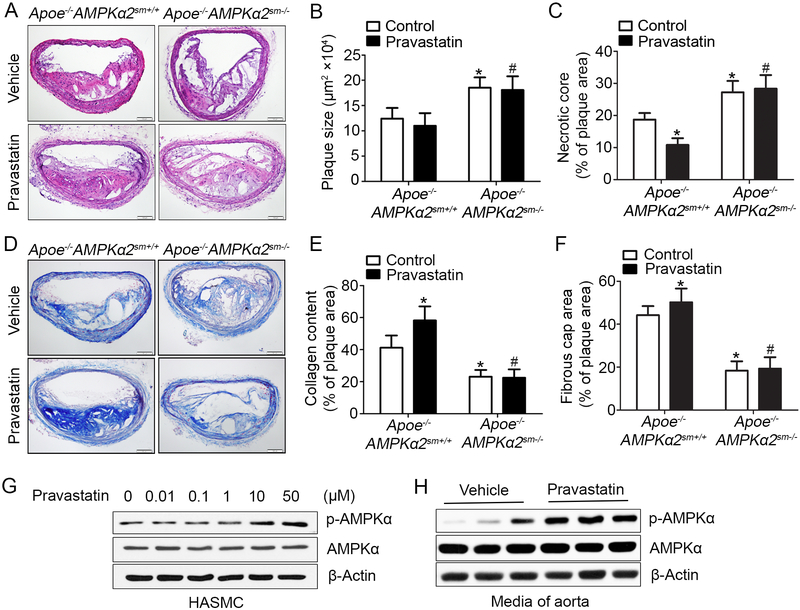
Figure 4. Pravastatin treatment alleviates western diet-induced plaque instability in Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ mice, but not in Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm−/− mice.
(A) Representative images from H&E staining of the BA in Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ and Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm−/− mice treated with or without pravastatin. Scale bar=100 μm. (B) Quantification of plaque size and (C) necrotic core size in the BA of Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ and Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm−/− mice treated with or without pravastatin. (D-E) Representative images and quantification of plaque collagen content in the BA based on Masson trichrome staining of Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ and Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm−/− mice treated with or without pravastatin. Scale bar=100 μm. (F) Quantification of fibrous cap area in the BA of Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ and Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm−/− mice treated with or without pravastatin. n=10 in each group. Values represent the means ± SEM. *, P<0.05 vs. Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ mice without pravastatin treatment. #, P<0.05 vs. Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ mice with pravastatin treatment. (G) Western blot analysis of pAMPKα (Thr172) in HASMC treated with 0.01–50 μM pravastatin for 24 hours. (H) Western blot analysis of pAMPKα (Thr172) in aorta from Apoe−/−AMPKα2sm+/+ mice fed with western diet for 10 weeks and treated with or without pravastatin for 4 weeks.