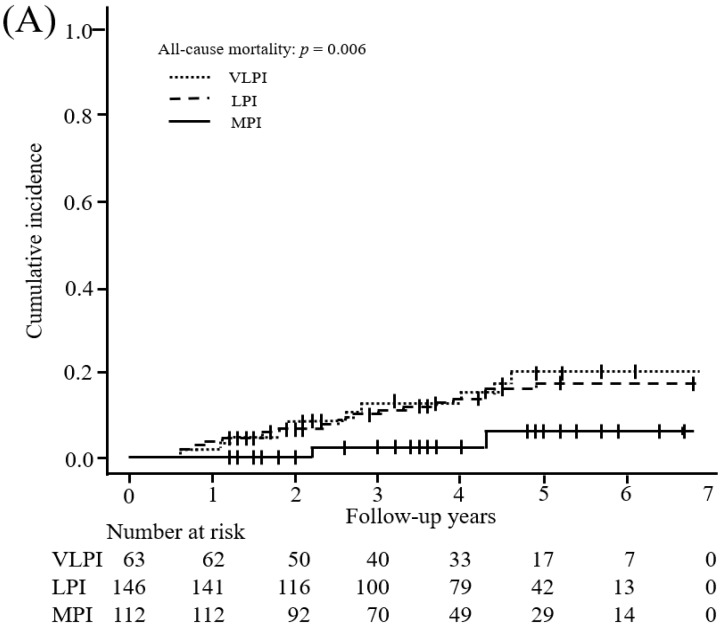
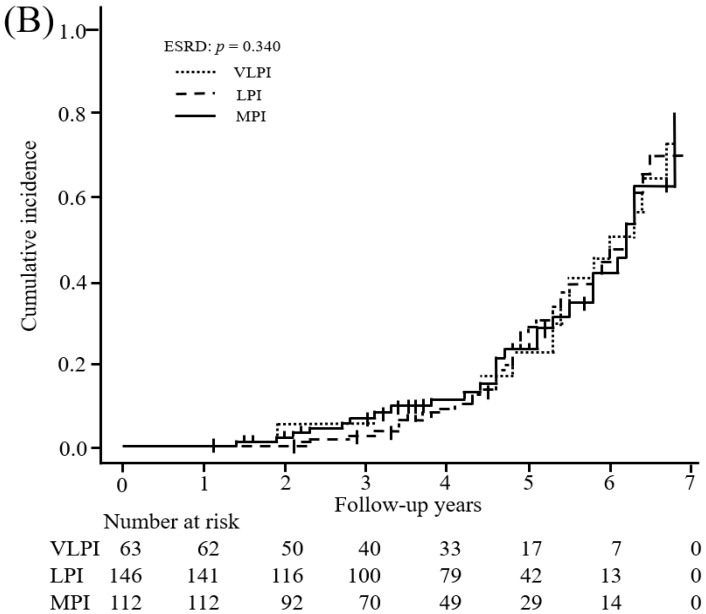
Figure 2.
Competing risk model for association between protein intake and the study endpoints. Cumulative incidences (95% confidence interval) of (A) mortality and (B) end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in the very low protein intake (VLPI), low protein intake (LPI), and moderate protein intake (MPI) groups were 0.199 (0.099 to 0.324), 0.170 (0.107 to 0.246), and 0.060 (0.018 to 0.138), respectively, and 0.801 (0.513 to 0.929), 0.695 (0.519 to 0.818), and 0.781 (0.259 to 0.956), respectively. Thirty-one patients were excluded because of death (n = 6) or development of ESRD (n = 25) within the first 6 months of follow-up. ESRD was defined as hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or kidney transplantation. Multivariable models included age, sex, BMI, CKD stage, and comorbidities (DM, CVD, and anemia) (Model 1).