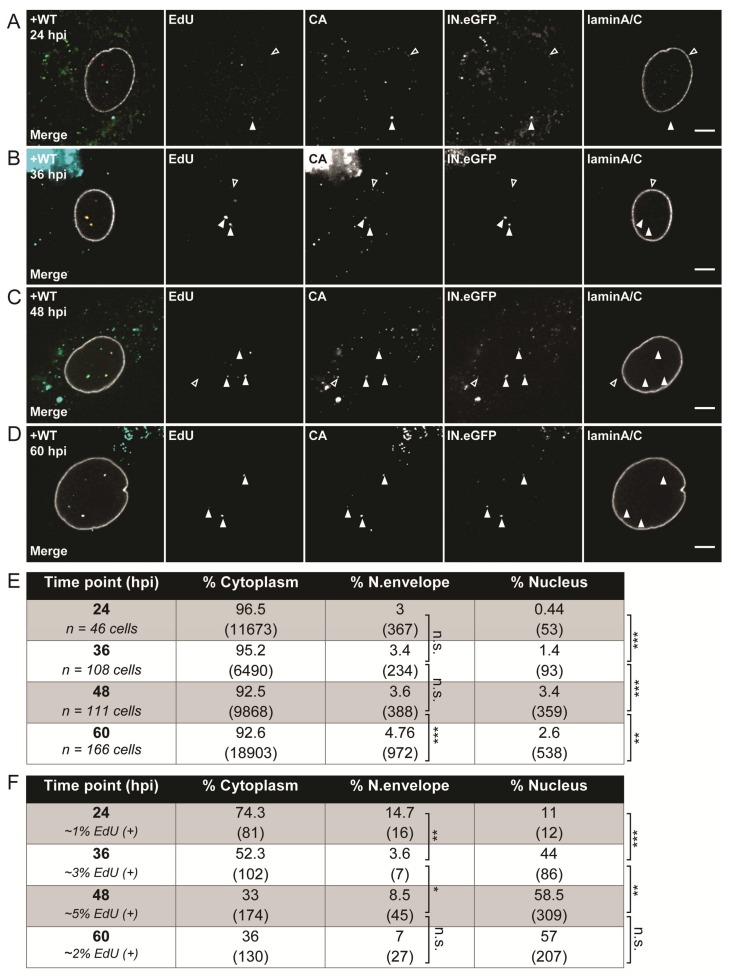
Figure 3.
Subcellular detection of HIV-1 reverse-transcription and pre-integration complexes (RTC/PIC). MDMs from four donors in three independent experiments were infected with 100 ng of CA of R5-pseudotyped HIV-1NL4-3 (IN.eGFP) in the presence of 10 µM 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU). At 24 h p.i., medium was changed and further viral entry was blocked by 5 µM MVC. Cells were fixed at 24 (A), 36 (B), 48 (C), and 60 h p.i. (D), click-labeled, and immunostained with anti-CA antiserum (cyan); the nuclear envelope was marked by immunostaining with anti-laminA/C antibody (white). EdU and IN.eGFP signals in the merged panels are represented in red and green, respectively. Exemplary complexes of different types are indicated by arrowheads: solid arrows indicate co-localizing EdU and IN.eGFP signals; empty arrows identify HIV-1 complexes lacking EdU signals. Scale bars represent 5 µm. (E) Proportion of IN.eGFP-positive objects in n cells in three subcellular localizations at different time points. Numbers of detected objects are given in parentheses. Proportions were compared using a two-tailed Z-test (α = 0.05); *** p < 0.0001; ** p < 0.002; n.s.: not significant. (F) Proportion of IN.eGFP- and EdU-positive objects from (E) in n cells in three subcellular localizations at different time points. Numbers of detected objects are given in parentheses. Proportions were compared using a two-tailed Z-test (α = 0.05); *** p < 0.0001; ** p < 0.005; * p = 0.022; n.s.: not significant.