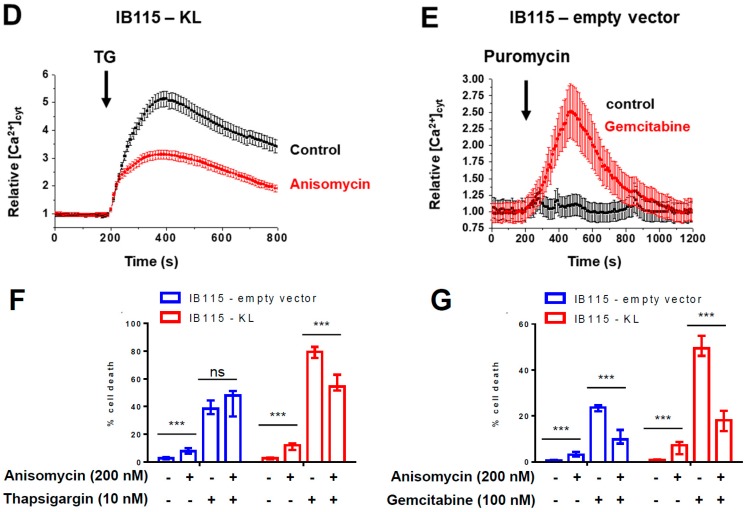
Figure 6.
In DDLPS cells, Klotho promotes reticular Ca2+-leakage and apoptosis by opening the translocon. (A–E) Variations of relative cytosolic Ca2+ concentration were monitored by fluorescence videomicroscopy in Fluo2-loaded cells. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (A–C) In a Ca2+-free HBSS medium, puromycin (25 µg/mL) was applied at 200 s on (A) IB115-empty vector cells, (B) IB115-KL cells, and on (C) IB115-KL cells pretreated 30 min with 200 nM anisomycin, a translocon-closing molecule. Each trace corresponds to the evolution of [Ca2+]cyt in one cell. (D) In a Ca2+-free HBSS medium, IB115-KL cells, pretreated (n = 114) or not (n = 76) with 200 nM anisomycin during 30 min, were stimulated at 200 s with TG (10 nM) to evaluate reticular Ca2+-leakage. Results are represented as means ± SD. (E) In a Ca2+-free HBSS medium, IB115-empty vector cells, pretreated (n = 78) or not (n = 81) with 100 nM gemcitabine during 24 h, were stimulated at 200 s with puromycin (25 µg/mL) to assess Ca2+-leakage through the translocon. Results are represented as means ± SD. (F,G) Cell death was measured by TMRM-staining and flow cytometry in IB115 cell lines pretreated for 1 h with 200 nM anisomycin and then incubated for 72 h with (F) 10 nM TG or (G) 100 nM gemcitabine. Histograms sum up (F) three and (G) four independent experiments. Data shown correspond to medians and IQR.