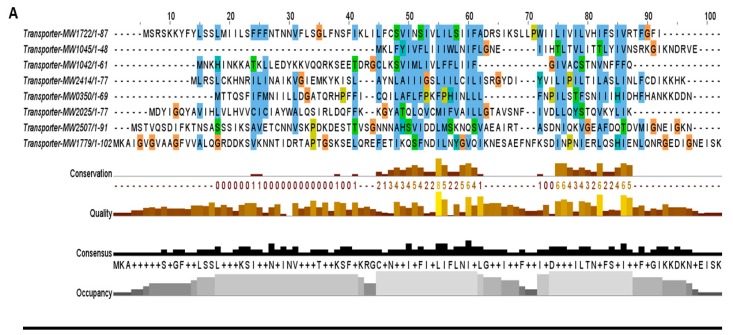
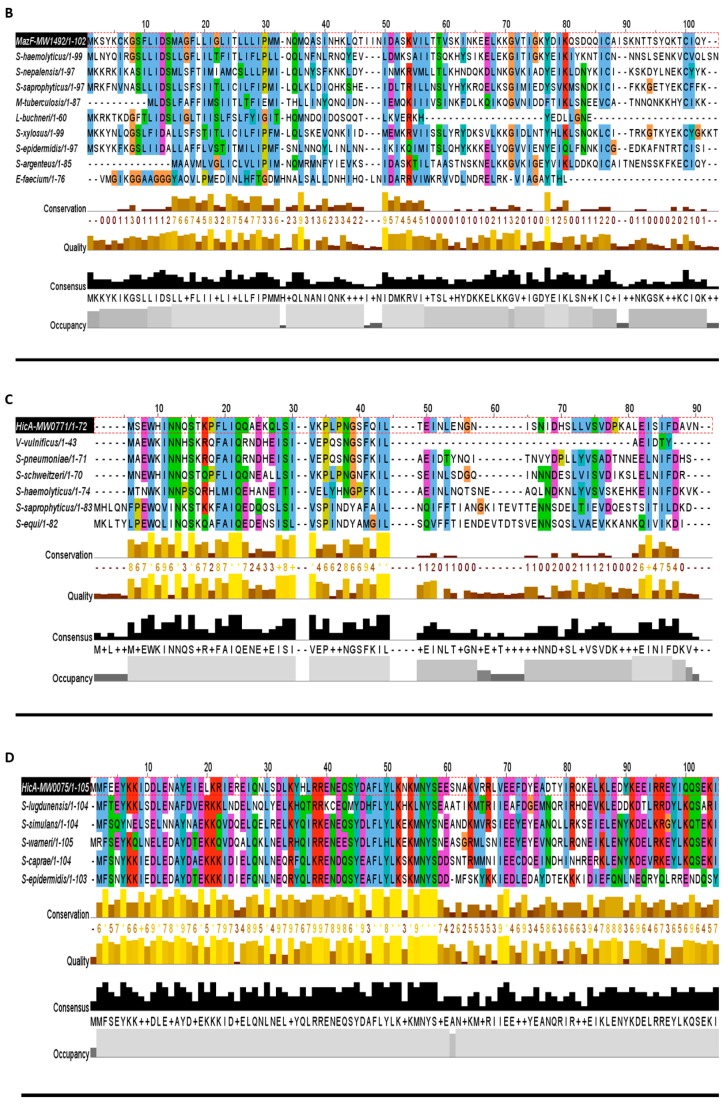
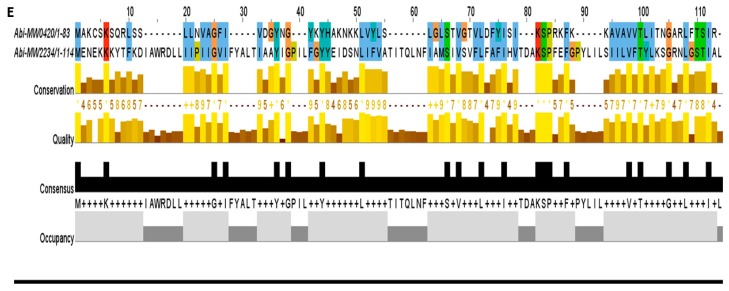
Figure 5.
The toxins were aligned by MUSCLE and sorted by pairwise alignment to close matching protein. (A) The transporter family toxins displayed less conservation among all TA families because each of the protein is associated with different secretion systems and transport pathways. The 15 residues (48–62 aa) are the highly consensus sites in this family. (B) Homologs of MazF toxin MW1492 were aligned that showed a high degree of conservation in M. tuberculosis, L. buchneri, E. faecium, and Staphylococcus species. The highly conserved region contains 25 residues (8–32 aa) at N-terminus. (C) The HicA toxin MW0771 homologs were detected in Vibrio vulnificus, S. pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus species. The 20 residues (11–30 aa) are the highly consensus sites in the homologs of MW00771 protein. (D) The homologs of MW0075 could not be detected in M. tuberculosis, L. buchneri, E. faecium, V. vulnificus, S. pneumoniae and B. cereus. The MW0075 toxin is a highly conserved protein in Staphylococcus species. (E) The two Abi toxins were aligned by pairwise alignment that showed 16% sequence similarity. Both Abi toxin homologs could be detected in different bacterial species.