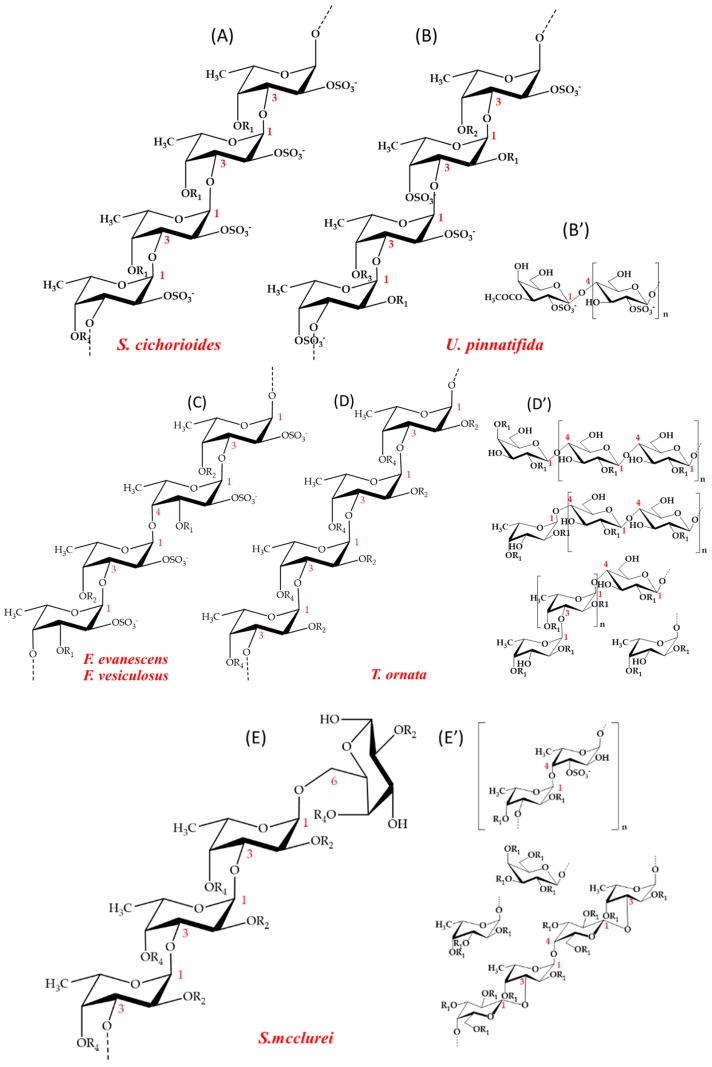
Figure 1.
Representative fucoidan structures of brown macroalgae Fucus evanescens, Fucus vesiculosus, Sargassum mcclurei, Turbinaria ornata, Saccharina cichorioides, and Undaria pinnatifida: (A) main chain of S. cichorioides composed of α(1→3)-l-fucosyls; (B) main chain of U. pinnatifida fucoidan also composed of α(1→3)-l-fucosyls; (B’) branches of U. pinnatifida fucoidan [11]; (C) main chain of F. evanescens [1] and F. vesiculosus fucoidan [8,9,10], both composed of α(1→3)- and α(1→4)-linked l-fucosyls; (D) main chain of T. ornata fucoidan composed of α(1→3)-l-fucosyls [13,14]; (D’) branches of T. ornata of α(1→3)-l-fucosyls or of β(1→4)galactosyls and mixed fucosyl-galactosyls; (E) main chain of S. mcclurei fucoidan made up of mainly α(1→3)-l-fucosyls [12]; and (E’) branches or inserts in the main chain of S. mcclurei fucoidan. In all fucoidan structures: R1: −H or −SO3−; R2: −H, −SO3− or H3COC−; R3: SO3−, H3COC− or branches; and R4: SO3− or branches.