Figure 4. rNT-DsrAI antisera bind the surface of class I H. ducreyi strains 35000HP and HMC50.
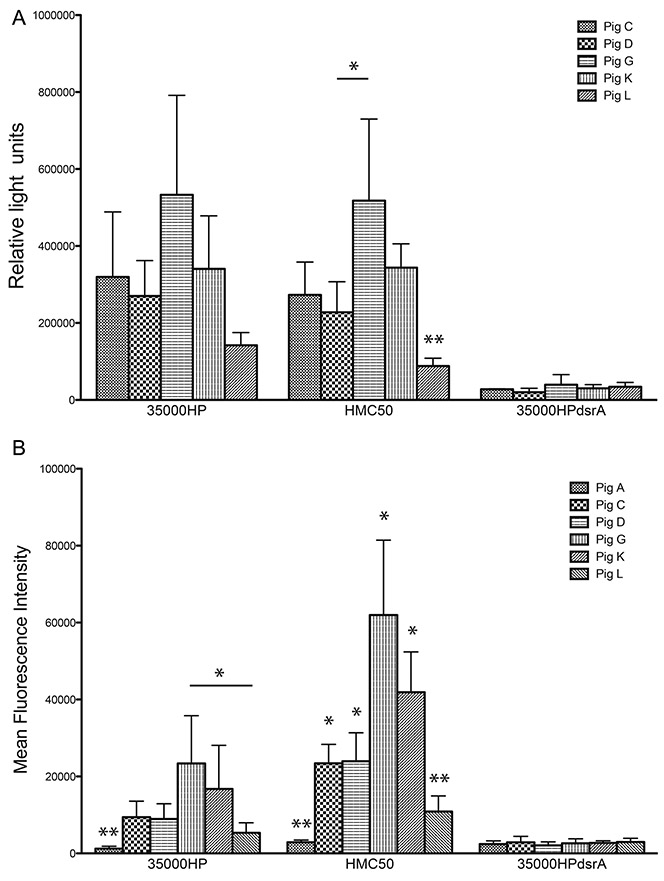
Antisera from the five rNT-DsrAI-vaccinated pigs were analyzed for binding to the bacterial cell surface using a whole cell-binding ELISA (A) and flow cytometry (B). A. Reactivity (mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments) of antisera to homologous strain 35000HP, heterologous strains HMC50, and isogenic dsrA mutant FX517 (35000HPdsrA). B. Binding of FITC-labeled rNT-DsrAI antisera IgG (from individual pigs C, D, G, K or L) and one animal receiving adjuvant only (pig A) to the surface of H. ducreyi, expressed as mean fluorescent intensity (MFI). Shown are means ± standard deviations of the MFI obtained from 4 independent experiments. For HMC50, all bars are statistically different from one another, except for pigs C and D, and G and K. The results presented in this figure reflect the reactivity of anti- rNT-DsrAI obtained one week after the 4th immunization, on the day of infection. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.05 as compared to all other bars in the same group, obtained using a unpaired t-test.
