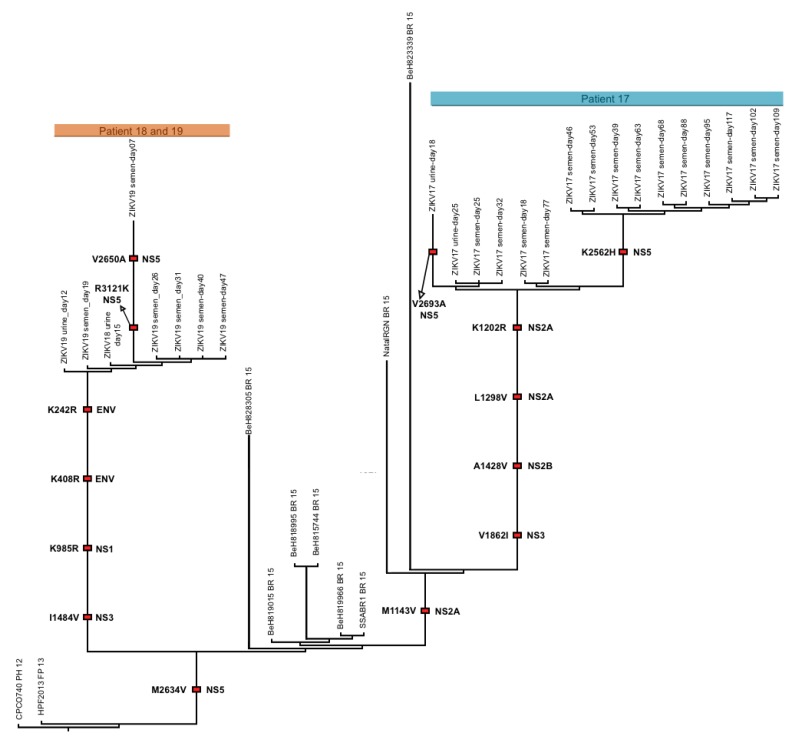
Figure 6.
Dendogram showing the most parsimonious unique amino acid changes with high consistency index (CI=1) (black framed red boxes). Reconstructions were made using a set of ZIKV polyproteins from African and Asian lineage viruses. Branch lengths are shown proportional to the number of most parsimonious reconstructions (MPR) of amino acid changes. Amino acid changes that define patient clades are shown as well as the viral proteins affected. Each patient clade (which had 100% support in ML tree shown in Figure S3) was supported by four synapomorphic changes. For both patients ZIKV19 and ZIKV17 changes were observed in the NS5 protein. Although we only show the results for selection detection methods for the three patients, elevated rates of non-synonymous changes were detected for all of the codons containing unique amino acid changes shown. The multiple EM for motif elicitation (MEME) algorithm detected significant positive selection (p-value = 0.03) acting on the codons containing the two NS5 changes observed during infection of patient ZIKV17. All MPRs were detected with FUBAR with a Bayes factor >3 and had elevated dN. Sites detected by 2-rates FEL had nonsynonymous changes in the absence of detectable synonymous changes. Significant negative, purifying selection was detected by all methods used on several sites of the polyprotein.