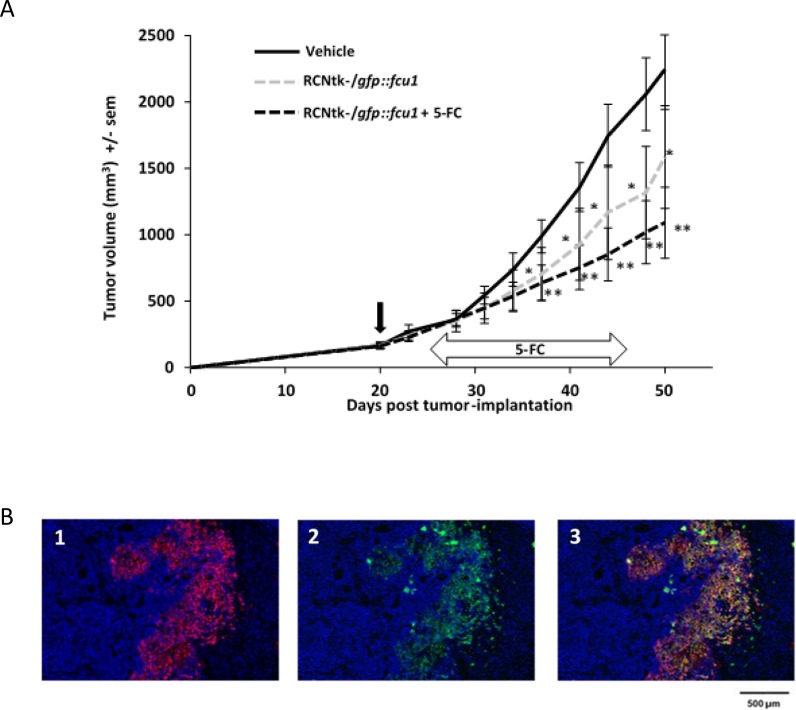
Figure 5. In vivo RCNtk-/gfp::fcu1 anti-tumor efficacy in a colorectal xenograft model.
(A) Growth evolution of human colorectal LoVo tumors. Swiss nude mice were implanted subcutaneously with LoVo colorectal cancer cells. Mice (n = 10/group) were injected IT with RCNtk-/gfp::fcu1 (107 pfu) on day 20 after tumor cell transplantation. Five days after viral injection, 5-FC was administered by gavage at 200 mg/kg/day for three weeks. Mice were monitored until sacrifice based on high tumor volume. Vertical black arrow indicates the time of virus injection and horizontal arrow indicates the duration of 5-FC treatment. Single star and double stars represent, respectively, P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 compared to the control group (vehicle). Results are expressed in mean tumor volume ± sem. (B) Immunodetection of FCU1 and RCNV proteins in the LoVo xenograft tumors. Immunostaining of the tumor was performed, as described in Materials and Methods, five days after IT injection of RCNtk-/gfp::fcu1 at 1 × 106 pfu. Cellular DNA was stained in blue with DAPI (1, 2 and 3), GFP::FCU1 protein was stained in red (1 and 3), and virus was stained in green (2 and 3). The merged picture is presented in 3.