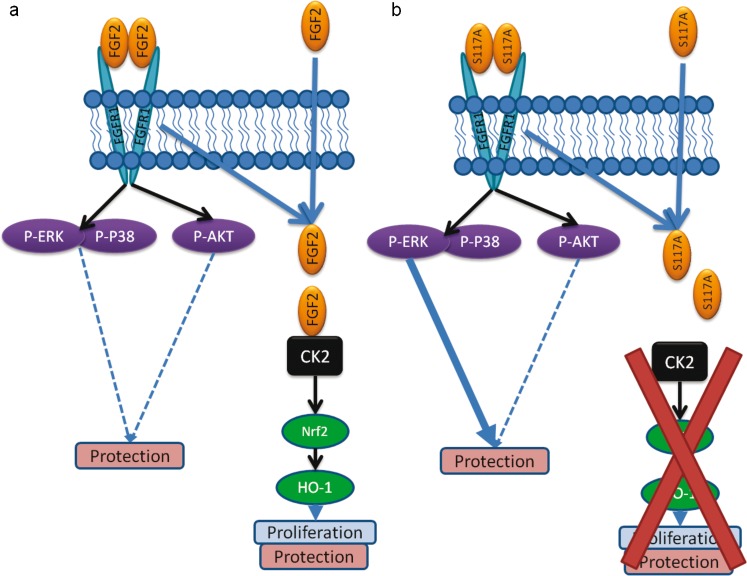
Fig. 6.
Diagramatic representation of the proposed signaling mechanisms mediating FGF2 versus S117A-FGF2 protection from Dox-induced damage. a Signaling by mitogenic FGF2, which activates FGFR1 and downstream kinases implicated in the modulation of cytoprotection, including ERK, p38 and AKT; the dotted lines indicate potential effects based on general literature but not studied here. Internalized FGF2 (via FGFR1-dependent or FGFR1-independent mechanism), interacts with and activates CK2 and CK2-dependent pathways (Nrf2, HO-1) that promote proliferation and proliferation-linked cytoprotection. b Signaling by S117A-FGF2, which lacks the ability to activate CK2 and the CK2-dependent effects on proliferation. S117-FGF2 retains the ability to activate FGFR1 and downstream kinases (ERK, p38 and AKT); of these, ERK was shown here to be required for S117-FGF2 protection in Dox-treated myocytes