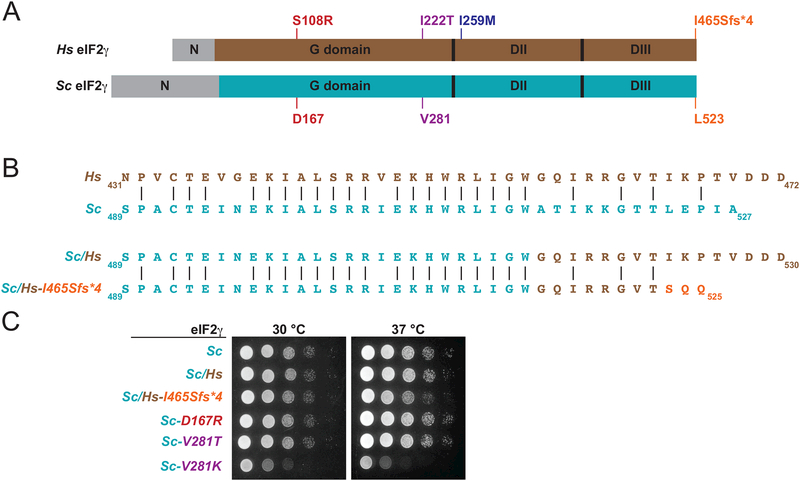
Figure 3. Impact of Mutations in Yeast eIF2γ on Cell Growth.
A: Schematics of human (top, brown) and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Sc, bottom, cyan) eIF2γ highlighting the N-terminal extensions (N), G domains and domains DII and DIII. Sites of mutations in human eIF2γ and the corresponding residues in yeast eIF2γ are labeled and colored as in Figure 2.
B: Alignments (top) of the C-terminal sequences of human (Hs, brown) and yeast (Sc, cyan) eIF2γ and (bottom) of a yeast/human eIF2γ chimera with either the native human C-terminus (Sc/Hs) or with the C-terminal frameshift mutation (Sc/Hs-I465Sfs*4).
C: Serial dilutions of yeast cells expressing, as the sole-source of eIF2γ, the indicated eIF2γ mutants were grown on minimal synthetic dextrose (SD) medium at 30 or 37 °C for 3 days.